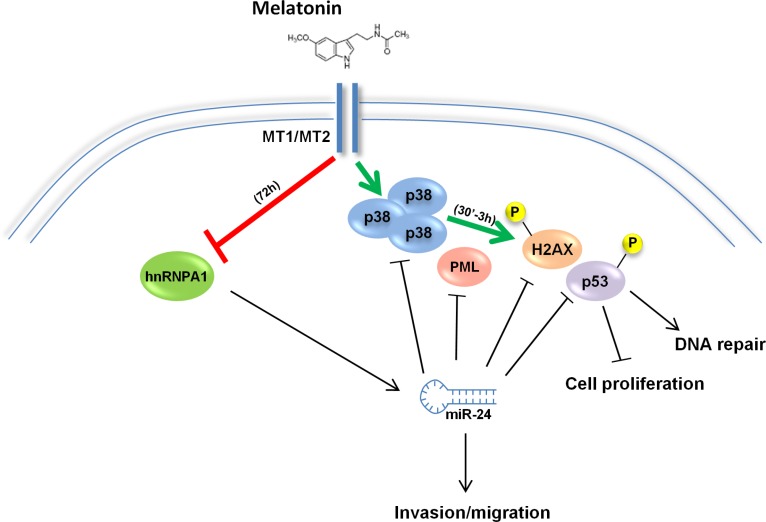
Figure 7. Model of melatonin activities.
By binding to its receptors (MT1/MT2), Melatonin induces p38 expression. With a fast kinetics (green arrow), Melatonin induces phosphorylation of p53 and H2AX thereby promoting DNA repair and inhibiting cell proliferation. Long-term activation of Melatonin receptors sustains p38 activation and leads to inhibition of hnRNP A1 (red arrow) thereby causing a decrease in miR-24, which results in p53, PML, H2AX and p38 activity reduction. Through downregulation of hnRNP A1 and miR-24, melatonin impairs the migrating capability of cancer cells.