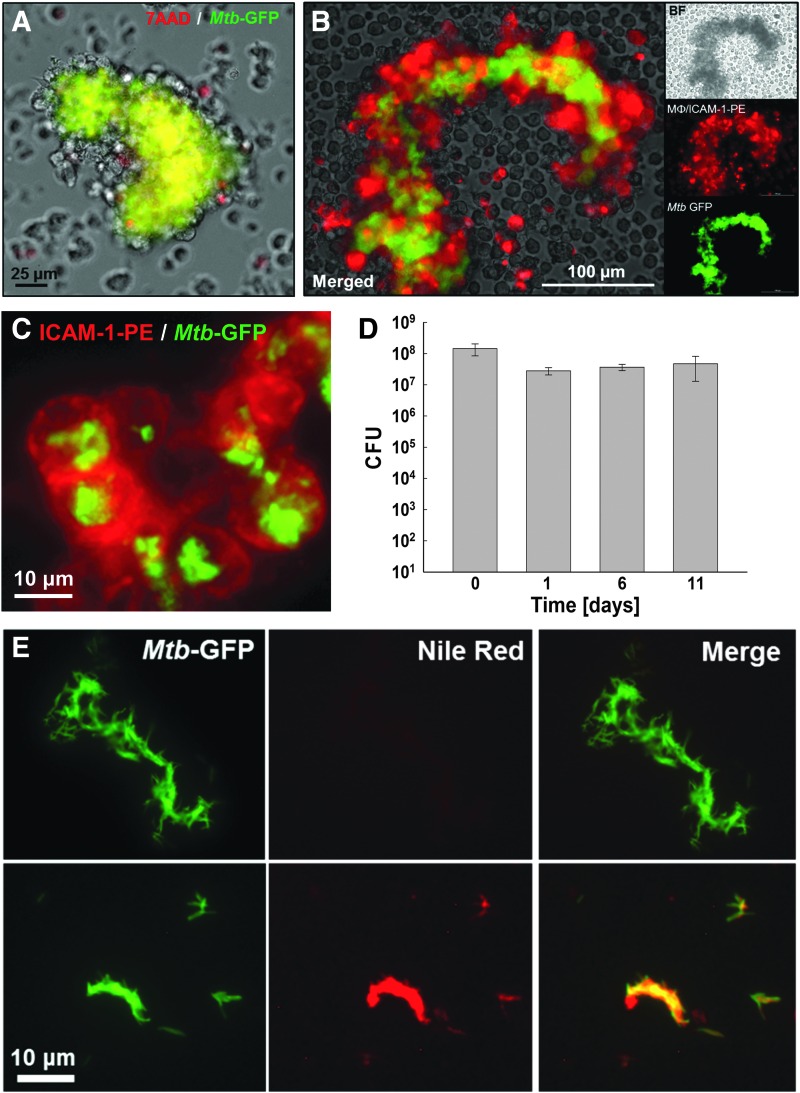
Fig. 2.
Biomolecular characterization of Mtb/macrophage aggregate structures. (A) Mtb/macrophage aggregate structures at 2 weeks postinfection were stained with 7AAD and a representative image is shown as merged GFP (Mtb) and RFP (7AAD) channels with bright-field image. (B) Mtb/macrophage aggregate structures at 2 weeks postinfection were stained with α-ICAM-1-PE mAbs and representative images are shown as merged GFP and RFP channels with bright-field images, or in separate channels alone. (C) Representative merged red and green channel fluorescence images of a group of viable macrophages derived from Mtb/macrophage aggregates stained with α-ICAM-1-PE antibody (red) that contain intracellular Mtb (green) at 2 weeks postinfection. (D) Intracellular survival of Mtb extracted from aggregate structures over a time course of 11 days was enumerated by CFU plating. (E) Mtb-GFP from in vitro broth-grown single-cell cultures (top panel) or extracted from Mtb/macrophage aggregates structures (bottom panel) 11 days postinfection were stained with Nile Red and representative images are shown as a merge of GFP and RFP channels, or in each individual channel. 7AAD, 7-amino-actinomycin D.