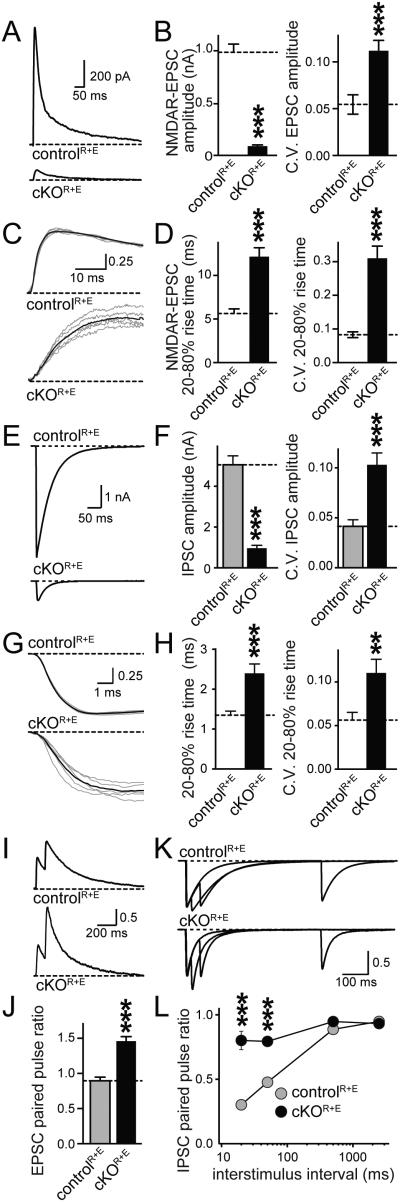
Figure 3.
Single action potential evoked synaptic transmission and release probability are strongly decreased upon disruption of the active zone
A, B. NMDAR-EPSCs were evoked by a focal stimulation electrode. Example traces (A) and quantitation of EPSC amplitudes (B) and their coefficient of variation (C.V.) in cKOR+E and controlR+E neurons are shown (controlR+E n = 24 cells/4 independent cultures, cKOR+E n = 26/4).
C, D. Sample traces (C) and quantitation (D) of EPSC rise times and their C.V. (n as in B). Individual sweeps are shown in grey and the average of all sweeps is shown in black. Traces are normalized to the average response.
E-H. Same analysis as in A-D for IPSCs (controlR+E n = 19/3, cKOR+E n = 19/3).
I,J. Analysis of NMDAR-EPSC paired pulse ratios (PPRs) in cKOR+E and controlR+E neurons. Sample traces (I, traces normalized to the first response) and quantitation (J) of the PPR at 100 ms interstimulus interval (controlR+E n = 23/4 independent cultures, cKOR+E n= 26/4).
K, L. Scaled sample traces (K, traces normalized to the first response) and summary data (L) of IPSC PPRs at variable interstimulus intervals (controlR+E n = 19/3, cKOR+E n = 19/3).
All data are means ± SEM; **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001 as determined by Student's t test in A-H, or by two-way ANOVA in L (genotype, interstimulus interval, and interaction p ≤ 0.001, p values of post-hoc Holm-Sidak tests are shown). All numerical data are in Table S3.