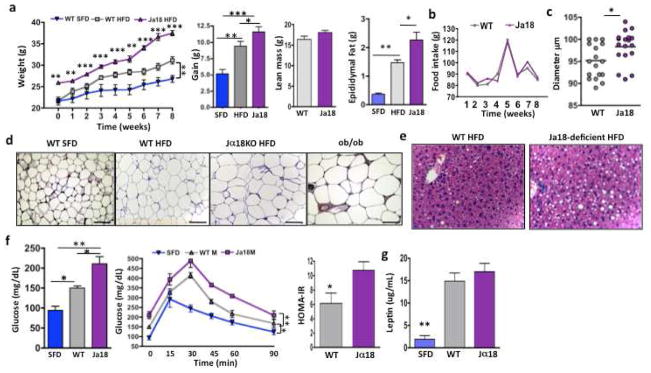
Figure 2. Impact of iNKT cell deficiency on weight gain, glucose tolerance, adipocyte size and number and fat accumulation in liver.
(a) Weight of Jα18−/− and wt mice on commencement of and during 8 weeks of HFD compared to wt on SFD (n=4 per group per week). Overall weight gain afer 8 weeks of HFD. Lean mass and epididymal fat pad weight of wt and Jα18−/− mice on HFD, wt mice on SFD are shown for comparison. (b) HFD food intake of wt and Jα18-deficient mice. (c) Adipocyte diameter was measured on osmium-fixed adipocytes with a particle counter. Adipocyte size from Jα18−/− and wt mice on HFD (4 samples per mouse, 4 mice per group). (d) Histology of adipocytes from epididymal fat. Adipocyte size from wt mice on SFD, wt mice and HFD and Jα18−/− mice on HFD. ob/ob mice also shown for comparison. Scale bars, 100μm. (e) Histology of fat infiltration in liver of wt and Jα18−/− mice on HFD (Representative of 4 individual experiments). (f) Fasting glucose (left), glucose tolerance (middle) and insulin resistance (right) in wt on SFD, wt on HFD, and Jα18-deficient mice on HFD for 6 weeks (n=4 per group, t tests, and 2 way ANOVA with Tukey for glucose tolerance tests). Insulin resistance as measured by HOMA-IR (t test). (g) Serum leptin levels in wt and Jα18-deficient mice on HFD compared to wt on SFD (n=4 per group, ANOVA). Graphs show mean+ s.d. *p<0.05, **, p<0.01, ***p<0.0001