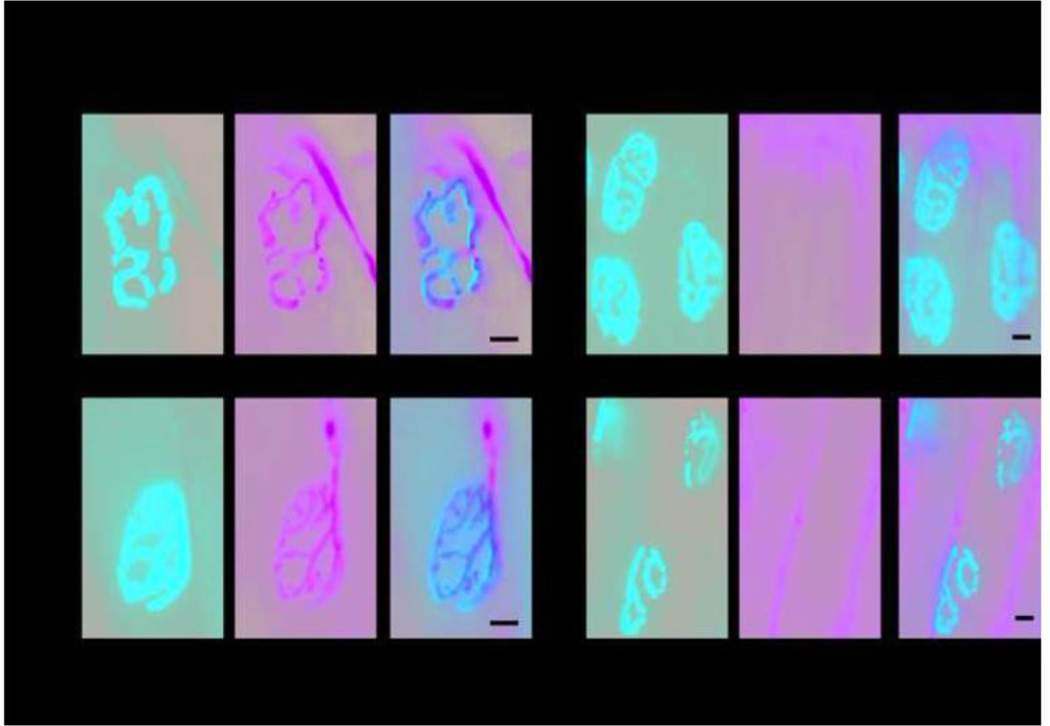
Figure 7. Morphology of the neuromuscular junction.
Serial sections of the extensor digitalis longus muscle of the hind limb from 1 year old Scn8a9J/9J mice and wild-type littermates were immunostained with antibodies to the neuronal proteins SV2 and 2H3 and with α-bungarotoxin to detect the acetylcholine receptor in the muscle endplate. The total number, morphology, and proportion of innervated NMJs did not differ between mutant and wildtype mice. A. Normal morphology of innervated neuromuscular junctions demonstrating the complex perforated morphology and close apposition of pre and post-terminal components. B. Regions with denervated endplates were apparent in mutant and wildtype mice. Scale bar, 10 µm.