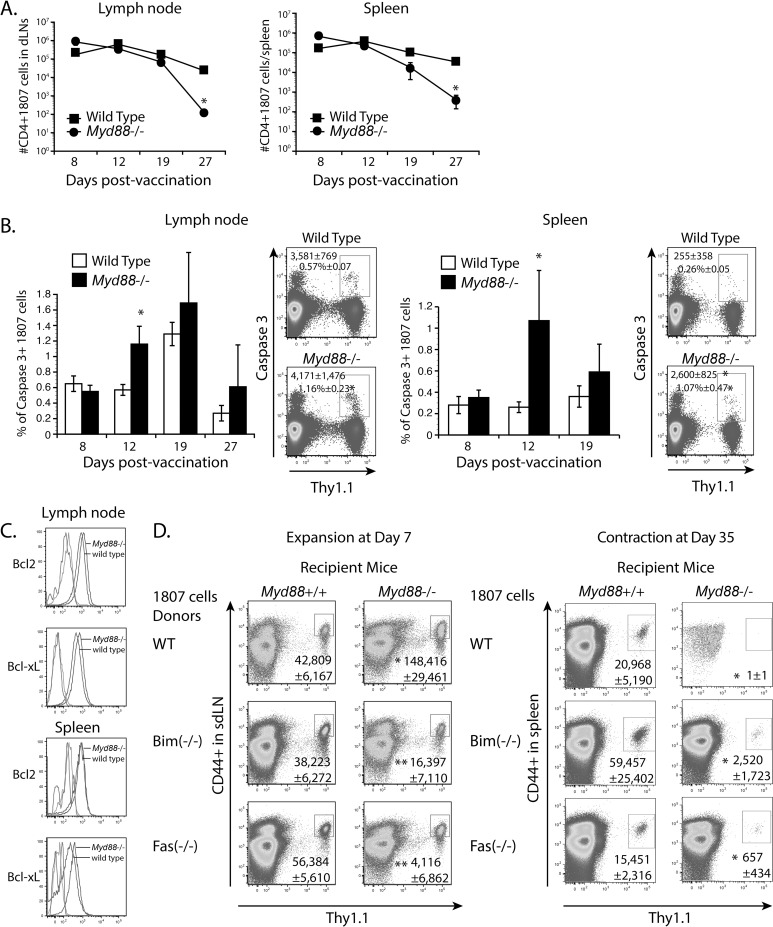
Fig 5. The role of extrinsic MyD88 for effector CD4+ T cell survival.
(A-C) Mice received 106 purified CD4+ T cells from naïve 1807 mice and were vaccinated with heat-killed yeast. (A) 1807 T cell contraction. At serial time intervals post-vaccination, the numbers of activated 1807 T cells were enumerated from the sdLN and spleen by FACS. * P < 0.05 vs. wild type control recipient mice. (B) Caspase 3 expression. Numbers in the dot plot indicate the numbers (top line) and frequencies (2nd line from top) of intracellular caspase 3 positive 1807 T cells within the CD4+ T cell gate at day 12 post-vaccination. * P < 0.05 vs. wild type control recipient mice. (C) The mean fluorescence intensity of Bcl2 and Bcl-xL expression in 1807 T cells transferred into wild type and Myd88 -/- recipients. Isotype controls are shown on the left of the graphs (unlabeled). (D) Adoptive transfer of naïve Bim-/- 1807 T cells and Fas-/- 1807 T cells into Myd88 -/- and wild type controls prior to vaccination. At days 7 and 35 post-vaccination, the numbers of adoptively transferred 1807 T cells were enumerated in the sdLN and spleen. Data are the mean ± SEM (n = 4–6 mice/group). Data are representative of two independent experiments. * P < 0.05 vs. corresponding wild type recipient mice. ** P < 0.05 vs. corresponding wild type 1807 cells.