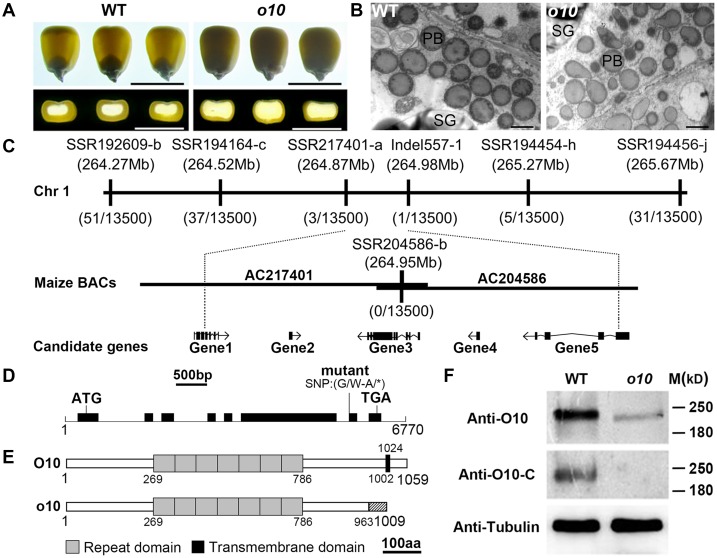
Fig 1. Map-based cloning and identification of O10.
(A) Light transmission and transverse sections of the wild-type (WT) and o10 kernels from the same F2 ear. Bars = 1 cm. (B) Observation of PBs in the wild-type and o10 developing kernels at 21 DAP by TEM. Bars = 1 μm. PB, protein body; SG, starch granules. (C) The o10 locus was mapped to a 110-kb region on chromosome 1 with five candidate genes. (D) Structure and mutation site of the O10 gene. The lines represent introns, and the black boxes represent exons. (E) Schematic diagram of the maize O10 and o10 protein structures. aa, amino acid. (F) Immunoblot comparing the accumulation of O10 in the wild-type and o10 mature kernels. Anti-tubulin was used as a sample loading control.