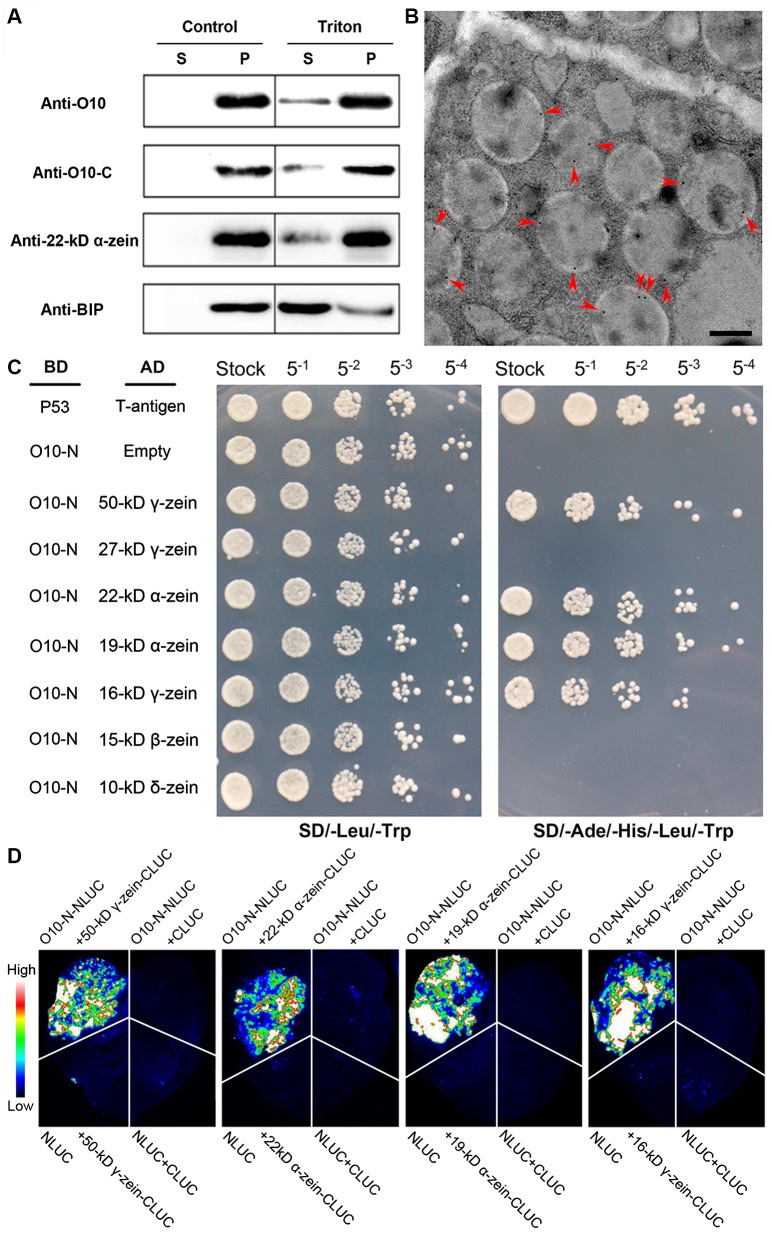
Fig 5. Localization of O10 in the PB and the Interactions between O10 and different type of zeins.
(A) Immunoblotting of O10 in the fraction of PB that was treated with Triton X-100. S, supernatant (the surrounding ER); P, pellet (the PB core). The fraction without Triton X-100 treatment was used as a negative control. Fractions were subjected to immunoblot analysis with antibodies against the N terminus of O10 (anti-O10), the C terminus of O10 (anti-O10-C), BIP (ER marker), or 22-kD α-zein (PB marker). (B) Immunolocalization of O10 in wild-type endosperm samples (21 DAP). The red arrowheads indicate O10 gold labeling on the PB; Bars = 0.5 μm. (C) O10-N represents the N terminus of O10 from 1–268 aa. The interaction between T-antigen and Human P53 was used as a positive control. The interaction between pGBKT7-O10-N and pGADT7-empty was used as a negative control. AD, activating domain; BD, binding domain. (D) LCI assay showing that the N terminus of O10 interacts with different types of zeins. Fluorescence signal intensities represent their interaction activities.