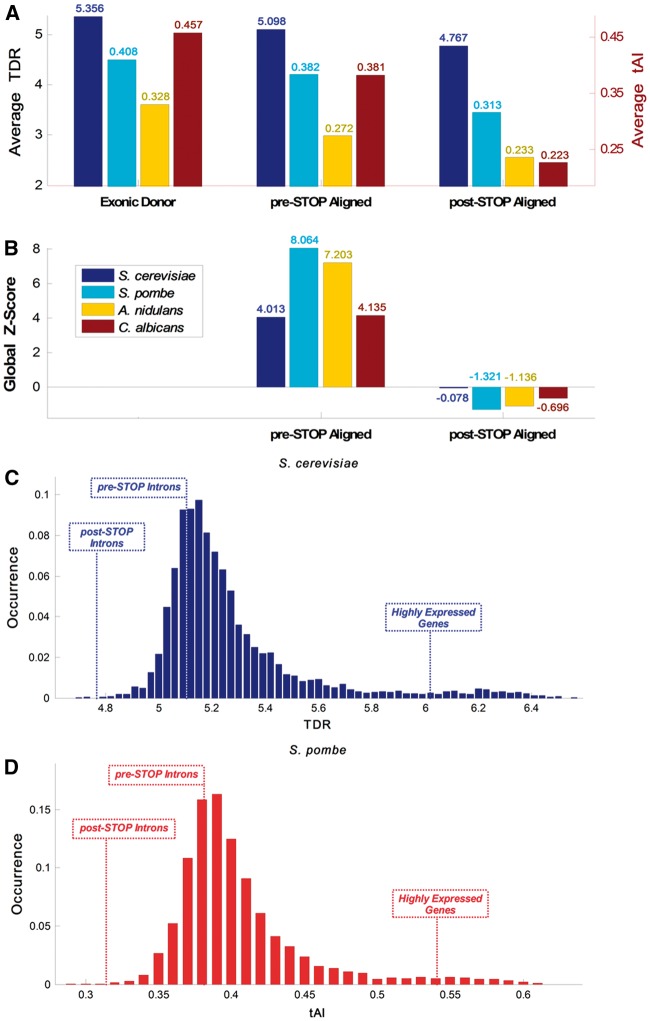
Figure 4.
CUB and translation efficiency summary. (A) Average TDR (S. cerevisiae) and tAI (S. pombe, A. nidulans, and C. albicans) in the Exonic Donor, pre-STOP and post-STOP domains of the examined organisms exhibit monotonic decrease in CUB over these three domains. (B) In all of the examined organisms the global Z-score at the pre-STOP domain is > 2 whereas the Z-score post-STOP domain is negative, supporting the hypothesis that there is selection for codons similar to some typical ORFs in the pre-STOP but not in the post-STOP domain, probably to optimize translation. (C) Distribution analysis of the S. cerevisiae whole genome demonstrate that the average TDR at the beginning of its introns is higher than in 23.87% of the genes (average value of 5.1); downstream from the first intronic STOP codon the values drop to be higher than only 0.07% of the genes (average value of 4.77); in comparison, average values of the top 300 highly expressed genes is 6.17. (D) Distribution analysis of the S. pombe whole genome demonstrate that the average tAI at the beginning of its introns is higher than in 31.02% of the genes (average value of 0.382); downstream from the first intronic STOP codon the values drop to be higher than only 0.1% of the genes (average value of 0.313); in comparison, the average value of the top 300 highly expressed genes is 0.542.