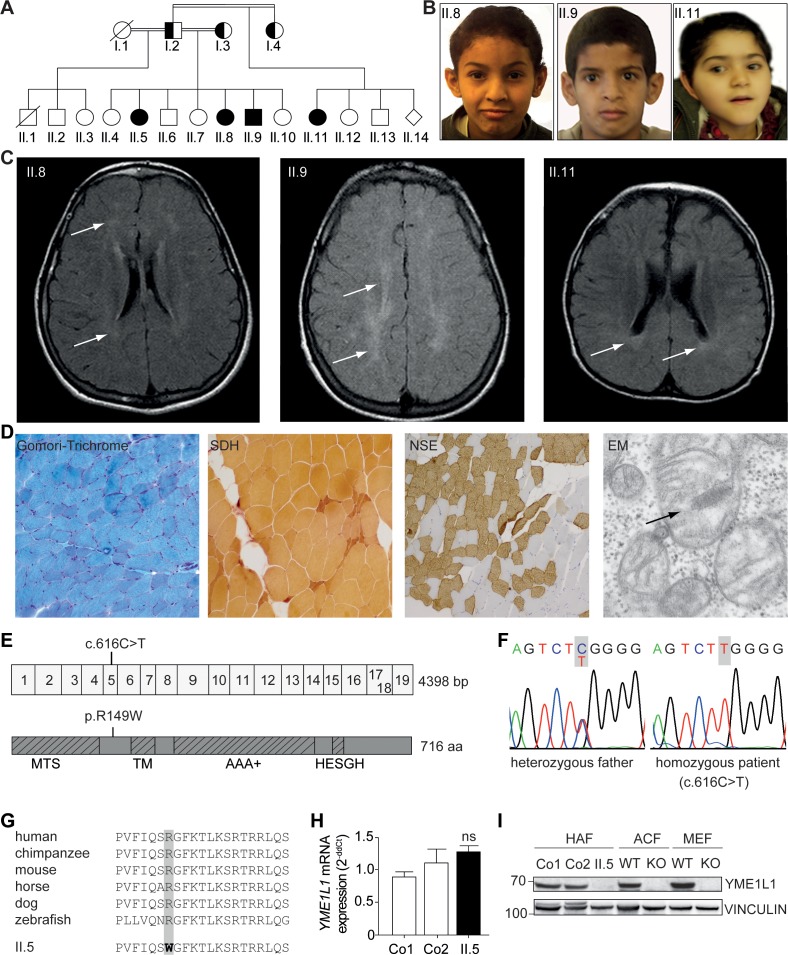
Figure 1. Phenotype and genotype of patients with YME1L1 mitochondriopathy.
(A, B) The four affected patients are children of healthy, consanguineous parents of Saudi Arabian decent (□ male; ○ female; ◊ unknown gender;  deceased;
deceased;  heterozygous, clinically not affected; ⚫/■ homozygous, affected;
heterozygous, clinically not affected; ⚫/■ homozygous, affected;  , consanguineous marriage). (C) Cranial MRIs reveal hyperintense changes (arrows) as a sign for leucencephalopathy, and cerebral atrophy (FLAIR, axial images). (D) Histological analysis of patient II.5 muscle biopsy specimen, from left to right: Gomori trichrome stain for muscle fibers revealed no conspicuous ragged red fibers indicative of a mitochondriopathy. Succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) and neuron specific enolase (NSE) staining revealed a neurogenic pattern with grouped fibers indicating denervation (magnification 200x). Electron microscopy (EM) revealed paracristalline inclusions (arrow) and altered cristae structure (“parking lots”, magnification 15,000x). (E) Whole exome sequencing discovered the homozygous mutation c.616C>T in exon 5 of the YME1L1 gene (NM_014263), localized at position 149 of the YME1L1 protein, and leading to an amino acid exchange of arginine to tryptophan in the mitochondrial targeting site (MTS; p.R149W, NP_055078). YME1L1 contains highly conserved domains: MTS, transmembrane domain (TM), ATPase domain (AAA+), motif of metalloprotease (Zinc) activity (HESGH). (F) Electropherogram depicting homozygous missense mutation in patient II.5, which is heterozygous in the father. (G) The mutation lies within a protein region, highly conserved throughout different species. (H) YME1L1 mRNA levels do not differ between patient and control primary human adult fibroblasts (Co, Control; II.5, patient II.5; ns, not significant; one-way ANOVA; p=0.2314; n=6 ) (I) Steady state levels of YME1L1 are below detection levels or profoundly reduced in cell lysates of patient II.5 YME1L1R149W; Yme1l1 knockout mouse fibroblasts serve as negative controls. YME1L1 protein levels in mitchondrial compartment fractions can be found Figure 1—figure supplement 1 (HAF, primary human adult fibroblasts; ACF, immortalized murine adult cardiac fibroblasts; MEF, immortalized murine embryonic fibroblast; Co, Control; II.5, patient II.5; WT, wild type; KO, Yme1l1 knockout, n=5).
, consanguineous marriage). (C) Cranial MRIs reveal hyperintense changes (arrows) as a sign for leucencephalopathy, and cerebral atrophy (FLAIR, axial images). (D) Histological analysis of patient II.5 muscle biopsy specimen, from left to right: Gomori trichrome stain for muscle fibers revealed no conspicuous ragged red fibers indicative of a mitochondriopathy. Succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) and neuron specific enolase (NSE) staining revealed a neurogenic pattern with grouped fibers indicating denervation (magnification 200x). Electron microscopy (EM) revealed paracristalline inclusions (arrow) and altered cristae structure (“parking lots”, magnification 15,000x). (E) Whole exome sequencing discovered the homozygous mutation c.616C>T in exon 5 of the YME1L1 gene (NM_014263), localized at position 149 of the YME1L1 protein, and leading to an amino acid exchange of arginine to tryptophan in the mitochondrial targeting site (MTS; p.R149W, NP_055078). YME1L1 contains highly conserved domains: MTS, transmembrane domain (TM), ATPase domain (AAA+), motif of metalloprotease (Zinc) activity (HESGH). (F) Electropherogram depicting homozygous missense mutation in patient II.5, which is heterozygous in the father. (G) The mutation lies within a protein region, highly conserved throughout different species. (H) YME1L1 mRNA levels do not differ between patient and control primary human adult fibroblasts (Co, Control; II.5, patient II.5; ns, not significant; one-way ANOVA; p=0.2314; n=6 ) (I) Steady state levels of YME1L1 are below detection levels or profoundly reduced in cell lysates of patient II.5 YME1L1R149W; Yme1l1 knockout mouse fibroblasts serve as negative controls. YME1L1 protein levels in mitchondrial compartment fractions can be found Figure 1—figure supplement 1 (HAF, primary human adult fibroblasts; ACF, immortalized murine adult cardiac fibroblasts; MEF, immortalized murine embryonic fibroblast; Co, Control; II.5, patient II.5; WT, wild type; KO, Yme1l1 knockout, n=5).
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.16078.002
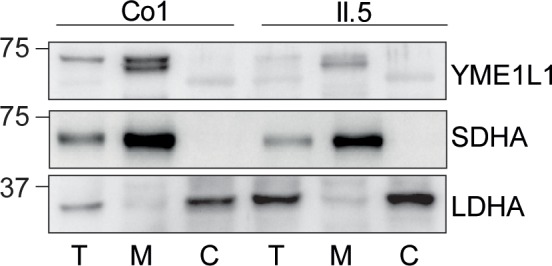
Figure 1—figure supplement 1. (I) YME1L1R149W signal is barely detectable in total cell lysates (T), significantly reduced in the mitochondrial (M) but not present in the cytosolic (C) fraction of patient primary human adult fibroblasts (Co, Control; II.5, patient II.5; SDHA, succinate dehydrogenase; LDHA, lactate dehydrogenase; n=3).