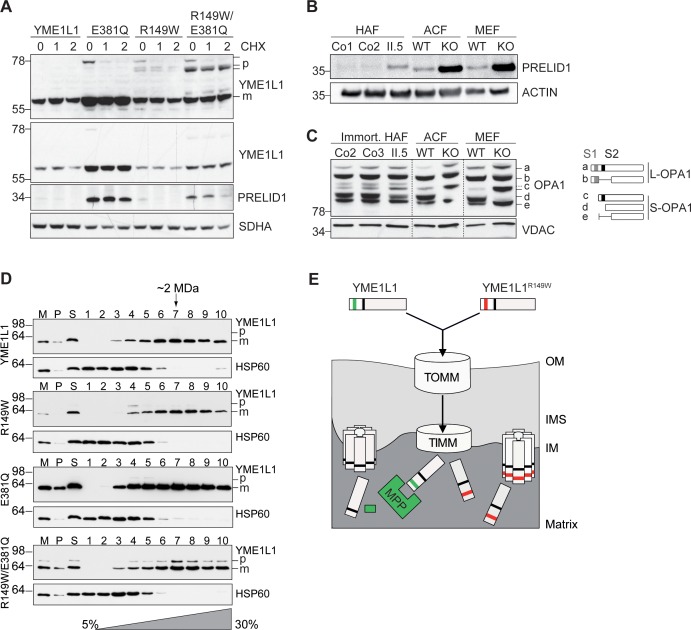
Figure 3. Mutation of arginine 149 destabilizes YME1L1 but retains residual YME1L activity.
(A) Stability of YME1L1 or YME1L1 mutant variants (R149W, E381Q and R149W/E381Q) expressed in Flp-In T-Rex HEK293T cells. The dominant negative E381Q mutation in the ATPase domain of YME1L1 prevents degradation of YME1L1R149W (E381Q, dominant negative mutation of ATPase domain; R149W, patient mutation; R149W/E381Q, double mutant; CHX, cycloheximide; h, hours; p, premature; m, mature; SDHA, succinate dehydrogenase; n=2). (B) Homozygous mutation in YME1L1 results in an accumulation of PRELID1 in the human patient. Yme1l1 knockout mouse fibroblasts serve as positive controls to demonstrate impaired proteolysis of PRELID1 (HAF, human adult primary fibroblasts; ACF, immortalized murine adult cardiac fibroblasts; MEF, immortalized murine embryonic fibroblast; Co, Control; II.5, patient; WT, wild type; KO, knockout; n=5). (C) Mutation of arginine 149 of YME1L1 impairs processing of OPA1 with a decrease of short OPA1 form d levels. The formation of OPA1 form d indicates residual YME1L1 activity in human patient fibroblasts (immort. HAF, immortalized human adult fibroblasts; ACF, immortalized murine adult cardiac fibroblasts; MEF, immortalized murine embryonic fibroblast; Co, Control; II.5, patient; WT, wild type; KO, knockout; n=6). The schematic diagram illustrates the proteolytic processing of OPA1 by YME1L1 on processing site 2 (S2) and OMA1 on processing site 1 (S1). The presence of long OPA1 forms (L-OPA1) is required for the maintenance of mitochondrial inner membrane fusion, whereas accumulation of short OPA1 forms (S-OPA1) is associated with accelerated fission. (D) Mitochondria-enriched membrane fractions from Flp-In T-Rex HEK293T cells expressing YME1L1 or YME1L1 mutant variants (R149W, E381Q and R149W/E381Q) were solubilized in digitonin and analyzed by sucrose gradient centrifugation. Fractions were collected and separated on SDS-PAGE for immunoblotting to detect high MW complexes of YME1L1. HSP60 complexes were used as a control (M, mitochondrial input, P, S, pellet and supernatant fraction after solubilization; HSP60, heat shock protein 60; E381Q, dominant negative mutation of ATPase domain; R149W, patient mutation; R149W/E381Q, double mutant). (E) Premature YME1L1/ YME1L1R149W is imported into the mitochondrial matrix via translocons of the outer mitochondrial membrane (TOMM) and inner mitochondrial membrane (TIMM). Here, MPP binds and cleaves the N-terminal mitochondrial targeting site (MTS) from premature YME1L1 but not YME1L1R149W, which then allows the mature and premature YME1L1R149W protein to assemble as proteolytic complex.