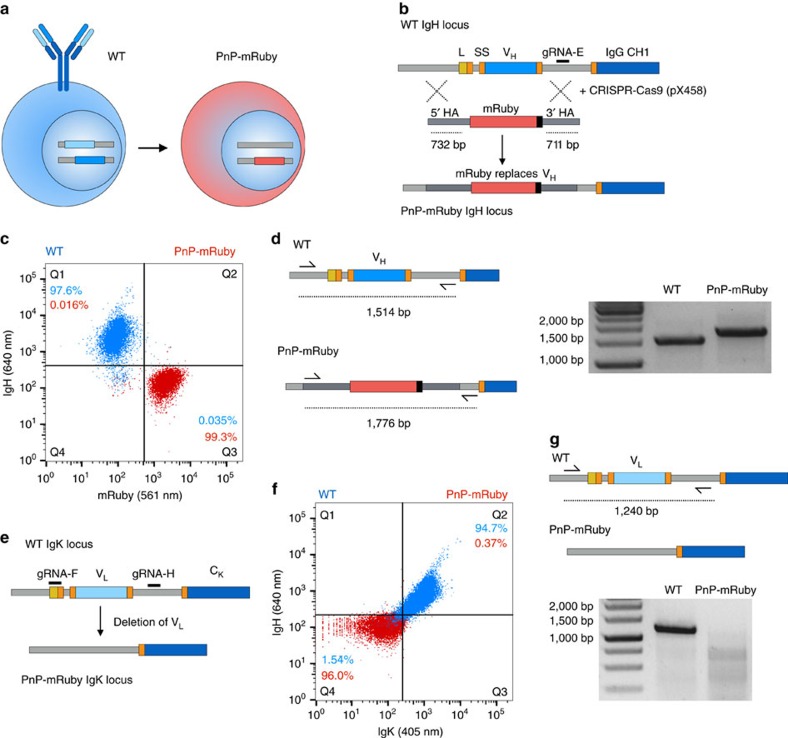
Figure 1. Generation of plug-and-(dis)play-mRuby cells.
(a) Schematic shows wild-type (WT) hybridoma cells expressing antibody that will be converted into plug-and-(dis)play (PnP)-mRuby cells. (b) Shown is the targeting of WT IgH genomic locus with the following annotations: leader sequence (L, yellow), mRNA splice sites (SS, orange), VH (blue) and IgG constant heavy region (CH1, dark blue). The Cas9 gRNA-E target site (black) is in the intron between VH and CH1. The donor construct consists of mRuby gene with a stop codon flanked by two homology arms (HA) of 732 and 711 bp. The PnP-mRuby IgH locus is generated by electroporation of WT cells with CRISPR-Cas9 plasmid and donor construct, which will result in HDR-based exchange of the VH region with mRuby. (c) Flow cytometry dot plot shows that WT cells are exclusively IgH-positive and mRuby-negative, where PnP-mRuby cells are exclusively mRuby-positive and IgH-negative. (d) PCR was performed on genomic DNA from WT and PnP-mRuby cells using a forward primer in 5′ HA and reverse primer that is external of the 3′ HA. Agarose gel shows the expected size of bands. The band from PnP-mRuby cells was extracted and Sanger sequencing confirmed mRuby exchange of the VH region (see Supplementary Fig. 3). (e) Shown is the targeting of WT hybridoma IgK locus with the following annotations: VL (light blue), and IgK constant light region (CK, dark blue), other annotations same as shown in a. Two gRNA target sites (black) are utilized to delete the VL region. (f) Flow cytometry dot plot shows WT cells are strongly IgH-positive and IgK-positive, where PnP-mRuby cells are exclusively IgH-negative and IgK-negative. (g) PCR was performed on genomic DNA from WT and PnP-mRuby cells using a forward primer 5′ of the gRNA-F site and reverse primer 3′ of gRNA-H site. Agarose gel shows the expected size of band for WT cells and nearly no amplification product for the PnP-mRuby cell line. Throughout this figure, WT cells correspond to clone WEN1.3 and PnP-mRuby cells correspond to clone 1E9.C3 (for more details, see Supplementary Table 1).