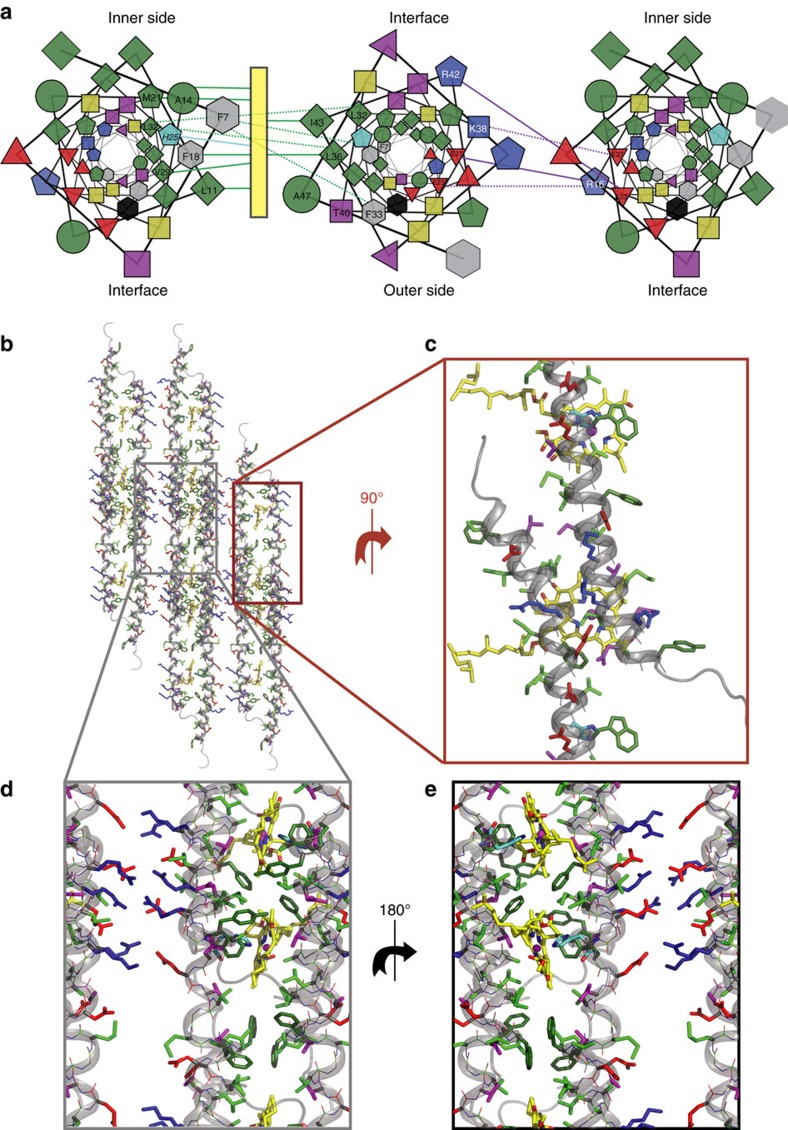
Figure 4. The CsmA baseplate structure.
(a) Helical wheel projections depicting three neighbouring helices viewed down the helix axis (colour code; green: hydrophobic, grey: aromatic, black: W, cyan: H, yellow: G, red: negatively charged, blue: positively charged). The symbols represent different residue types: G (circle), S/T/G/K (square), I/L/V (diamond), F/Y/W (hexagon), H/M/R (pentagon), and D, E, and Q/N (triangle pointing up, down and left, respectively). Purple lines indicate electrostatic interactions between oppositely charged residues, green lines highlight residues closely located to the BChl a pigment (yellow rectangle), while dotted lines represent hydrophobic packing between amino acids. The residues present on outer and inner side are annotated as well as the interface between two helices related by translational symmetry. (b–e) Molecular representation of the baseplate showing CsmA with cartoon and lines and side chains with sticks for the central residues 6–48. BChl a are shown as yellow sticks with N and O coloured in blue and red, respectively, hydrogen atoms are omitted for clarity. The colour code is the same in (a) except G is green and aromatic residues are shown with a darker green. (b) top view, (c) zoom on the translation interface, (c–e) zoom on the two interfaces viewed from the outer and inner side (the phytyl chains show here) of the carotenosome, respectively. See also Fig. 5.