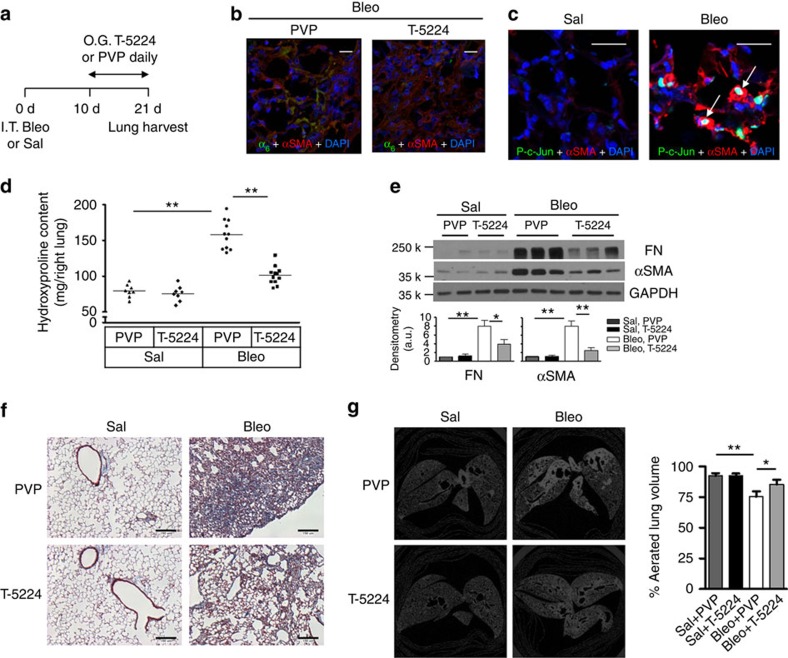
Figure 5. Pharmacological inhibition of c-Fos/c-Jun protects mice against bleomycin injury-induced experimental lung fibrosis.
(a) Animal experimental design. (b) Overlaid confocal immunofluorescent images show α6-expression (green) in αSMA-positive lung myofibroblasts (red) in mice with treatments as indicated. Nuclei were stained by DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 20 μm. (c) Overlaid confocal immunofluorescent images show phospho c-Jun (green) in the nuclei of αSMA-positive lung myofibroblasts (red) (arrows) in mice treated with saline or bleomycin. Nuclei were stained by DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 20 μm. (d) Quantification of hydroxyproline contents in right lungs of C57BL6 mice in four groups: Sal+PVP, Sal+T-5224, Bleo+PVP and Bleo+T-5224. Results are the means ±s.d. (e) Quantification of FN and αSMA protein expression in left lungs by immunoblot. Shown are representative blots. (f) Representative images for trichrome staining of collagens in paraffin-embedded lung tissue sections. Scale bar, 150 μm. (g) Shown are representative images for ex vivo mid-lung transaxial μCT scans. The average percentages of aerated lung volumes are shown in the bar graph (n=5 mice per group). Results are the means±s.d.; *P<0.05 and **P<0.01; one-way analysis of variance. O.G., oral gavage.