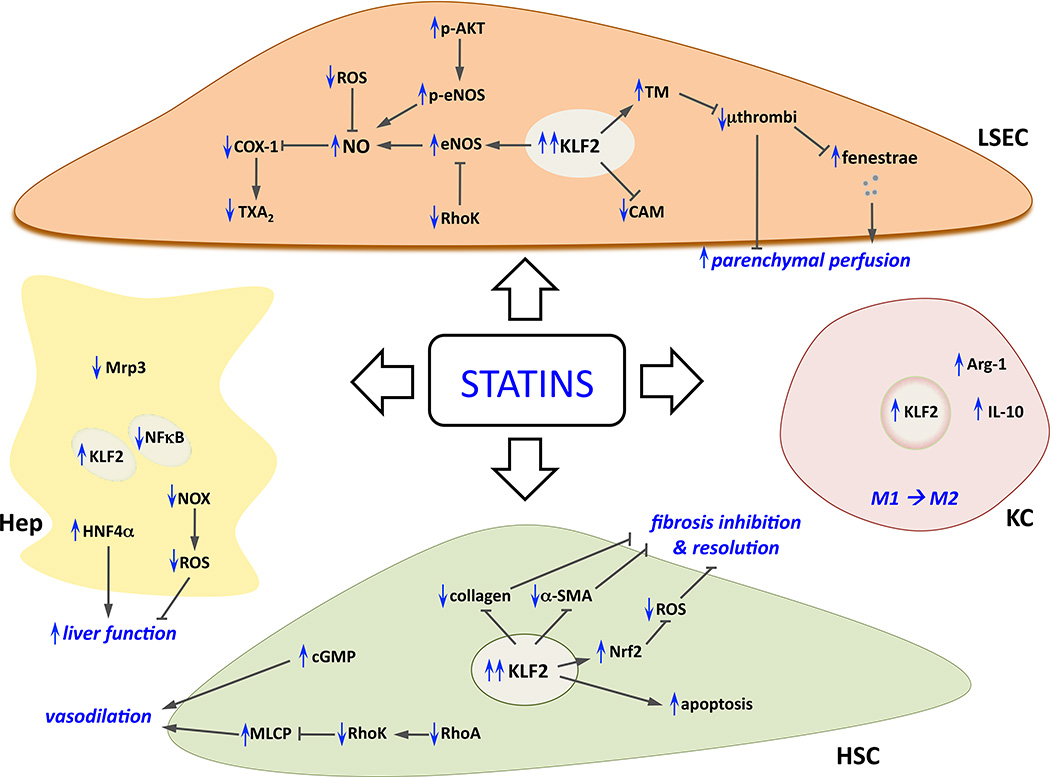
Figure 2. Effects of statins on sinusoidal cells.
Summary of cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying the beneficial effects of statins in liver cells (in blue, modifications due to statins administration). Please note that to simplify the figure paracrine interactions between statin-improved cells are intentionally omitted, complete explanation can be found along the text. α-SMA; smooth muscle actin alpha; Arg-1, arginase-1; CAM, cell adhesion molecules; cGMP, cyclic guanosine monophosphate; COX-1, cyclooxygenase-1; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; HNF4α, hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha; KLF2, Kruppel-like factor 2; MLCP, myosin light chain phosphatase; Mrp3, ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 3; NFkB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NO, nitric oxide; NOX, NADPH oxidase; Nrf2, nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2; ROS, radical oxygen species; TM, thrombomodulin; TXA2, thromboxane A2.