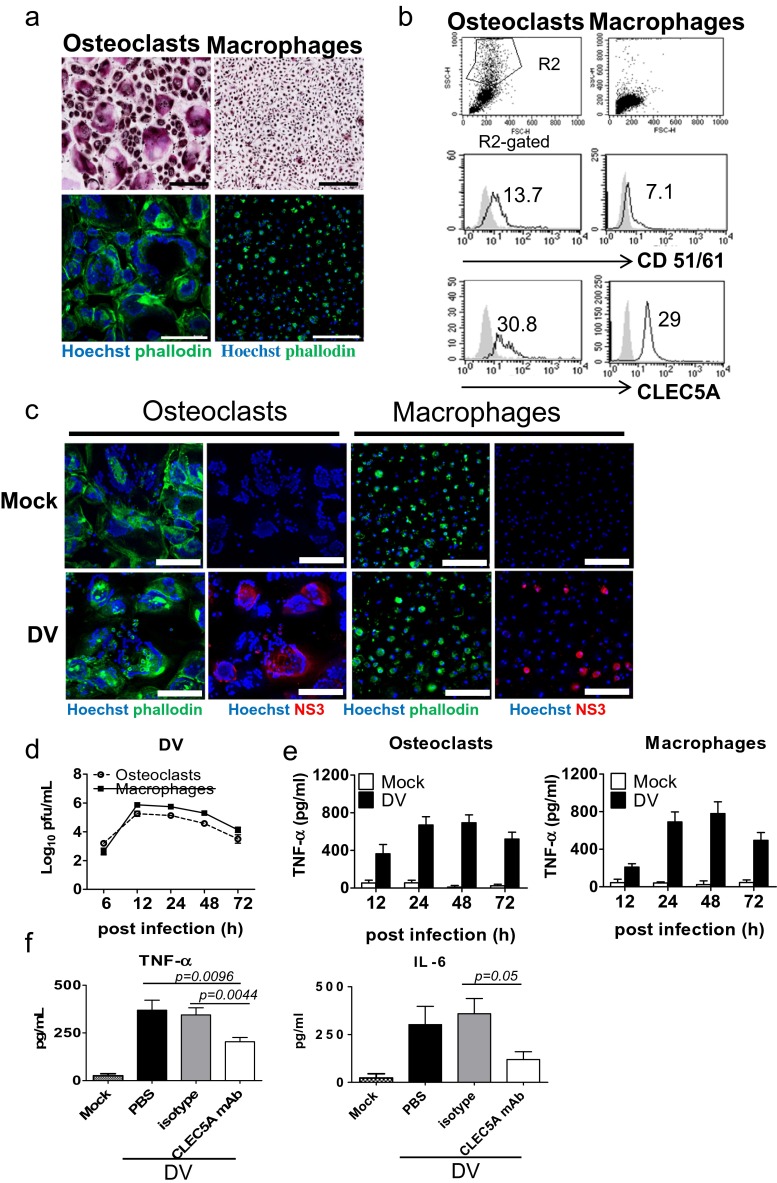
Fig. 1.
Osteoclasts are susceptible to DV infection and secrete proinflammatory cytokines via CLEC5A. a Human osteoclasts (with multinucleated, left) and macrophages (right) with TRAP (upper, purple red color) and phalloidin (lower, green color) staining, respectively. Scale bar, 200 μm. b Detection of osteoclast markers (CD51/61) and CLEC5A in human osteoclasts and macrophages by flow cytometry (gray shadow: isotype control; mean fluorescence intensity of each antibody staining was indicated). c Human osteoclasts and macrophages were infected with DV, and viral antigen NS3 (red color) was detected by immunofluorescence staining at 24 h postinfection. Cells were countered stained with Hoechst (blue) and phalloidin (green). Scale bar, 200 μm. d Viral titers in culture supernatants of human osteoclasts and macrophages were determined by plaque assay. e TNF-α secretion from DV-infected human osteoclasts (2 × 104/well) and macrophages (2 × 104/well) were determined by ELISA. f DV-induced secretion of TNF-α and IL-6 from human osteoclasts were inhibited by anti-CLEC5A mAb (clone: 3E12A2, 1 μg in the 200 μl/well). Supernatants were harvested at 24 h postinfection to determine cytokine levels by ELISA. Data were collected and expressed as mean ± SEM from at least three independent experiments. For f, ANOVA tests were performed and all the infections were performed at M.O.I. = 5