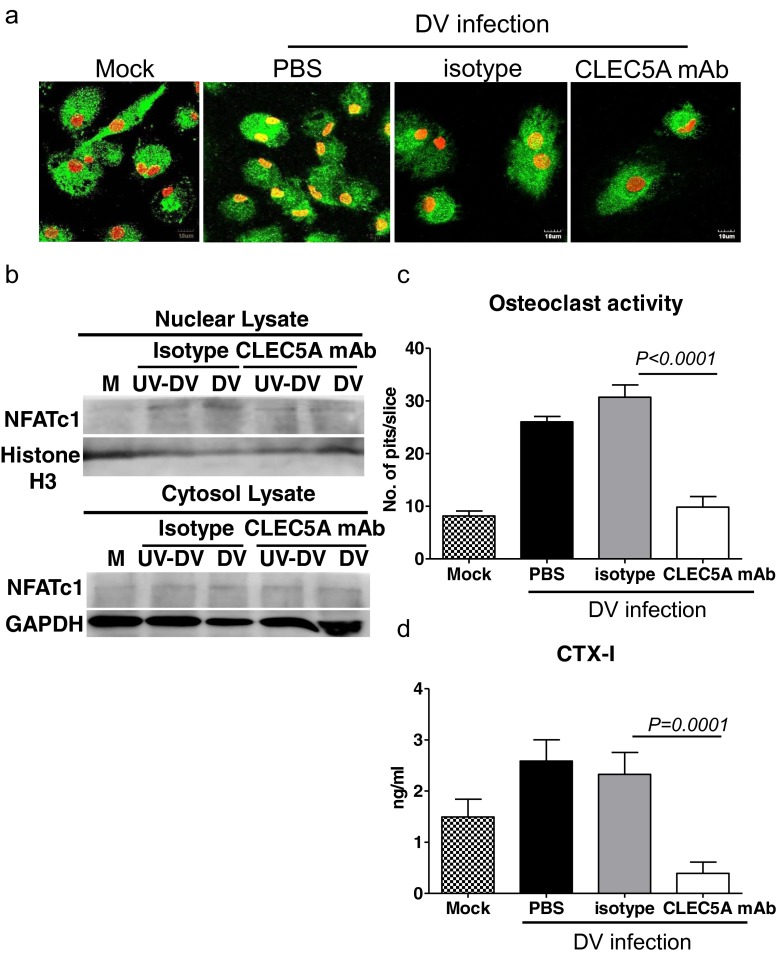
Fig. 3.
DV activates osteoclasts and upregulates osteolytic activity via CLEC5A. a Human osteoclasts (1 × 105/well) were preincubated with anti-CLEC5A mAb or isotype control, followed by DV infection. Cells were fixed at 24 h postinfection for immunofluorescence staining and were examined under a confocal microscope (Olympus FV1000). Scale bars, 10 μm. Green color: NFATc1; red color: Hoechst 33342; yellow color: merge of NFATc1 (green) and Hoechst 33342 (red). b Human osteoclasts (5 × 106) were preincubated with anti-CLEC5A mAb or isotype control, followed by DV infection. Cells were harvested at 12 h postinfection for WB analysis. c Determination of osteolytic activity by “pit formation” assay. Mature human osteoclasts were seeded on the bone slices and incubated with DV for 2 h in the presence of isotype control or CLEC5A mAb. The resorbed areas (pits) were examined under a microscope (Nikon) at day 6 after DV infection. Five images per each bone slice were randomly photographed, and the resorbed areas were counted and represented as mean ± SEM (under each picture) from three independent experiments. d Supernatants from bone slices incubated with human osteoclasts and DV were harvested at day 6 after DV infection to determine C-telopeptide of type I collagen (CTX-1) level by ELISA (CrossLaps for Culture). Data were collected and expressed as mean ± SEM ANOVA tests were performed and all the infections were performed at M.O.I. = 5