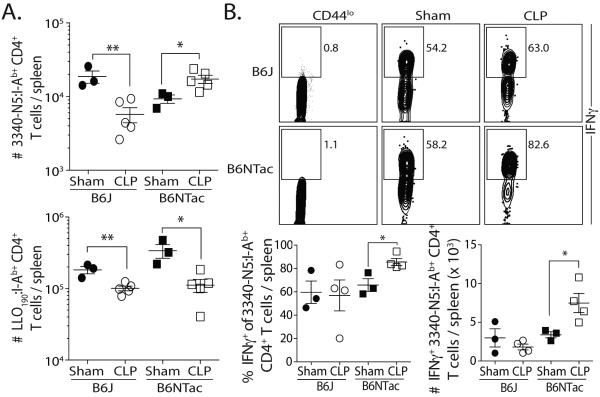
Figure 5.
SFB colonization changes the function of SFB-specific CD4 T cells in sepsis survivors. (A-B) B6J and B6NTac mice were infected with att. Lm-SFB (107 CFU in 0.1 ml i.v.) 30 d after sham or CLP surgery. (A) Proliferative capacity – The number of LLO190- and SFB-specific CD4 T cells was determined in the spleen 7 d after infection. (B) Functional capacity – 7 d after infection, splenocytes were stimulated for 4 h with PMA/ionomycin. The samples were enriched for SFB-specific CD4 T cells and IFNγ production was determined. Representative flow plots show the frequency of SFB-specific CD4 T cells producing IFNγ. The frequency and number of IFNγ+ SFB-specific CD4 T cells are graphed. Statistical significance in A-B was determined using group-wise, one-way ANOVA analyses followed by multiple-testing correction using the Holm-Sidak method, with α = 0.05. Data shown represent 2 independent experiments, with 3-5 mice/group in each experiment.