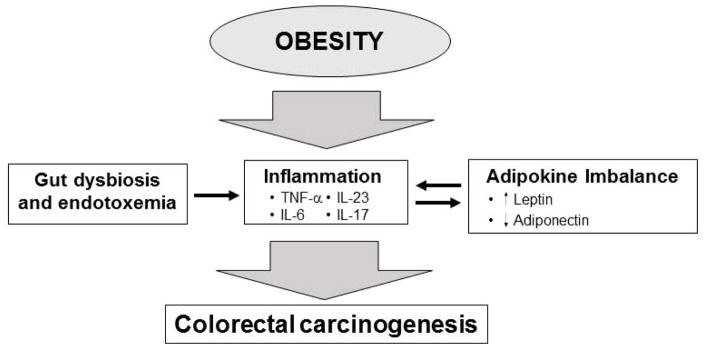
Figure 2. Obesity and colorectal cancer.
Obesity is associated with changes in the intestinal microbiome and dysfunction of the intestinal barrier. Gut dysbiosis and endotoxemia promotes inflammation through the upregulation inflammatory cytokines, particularly IL-6, TNF-α, IL-17 and IL-23, which promote CRC carcinogenesis. Obesity-associated changes in leptin and adiponectin also leads to increased inflammation and CRC carcinogenesis.