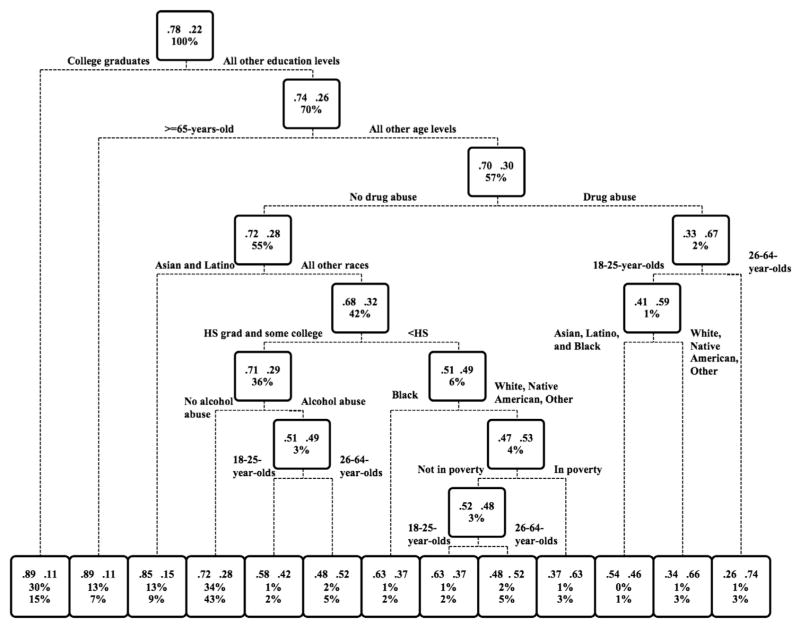
Fig. 3.
A pruned, weighted classification and regression tree (CART) model of associations between current (past 30 days) smoking status and the following eight risk factors in the U.S. adult (≥18 years of age) population: educational attainment, age, race/ethnicity, past year drug abuse/dependence, past year alcohol abuse/dependence, annual income below federal poverty level, and past year mental illness. Results from a saturated model were “pruned” using CART analytic software to reduce complexity (R Core Team, 2013). Rectangles (nodes) represent smoking prevalence rates for the entire population (top-most node) or population subgroups (all others nodes). Nodes also list the proportion of the adult population represented. Using the root node as an example, 78% of the population are non-smokers, 22% smokers, and this node represents 100 of the U.S. non-institutionalized adult population. Lines below nodes represent the binary “yes”–”no” branching around particular risk factors and risk-factor levels, with subgroups in whom the risk factor/level is present moving leftward and downward and those in whom it is absent moving rightward and downward for further potential partitioning based on additional risk factors/levels. The bottom row comprises terminal nodes (i.e., final partitioning for a particular subgroup). Note that minimal terminal node size was set to ≥1000 individuals. Terminal nodes contain the same information as the other nodes plus the percent of all adult current smokers represented by that node. Percent of current smokers represented is calculated by the following equation: % total population represented by a node × smoking prevalence in that node/smoking prevalence in the entire study sample × 100. Tallying % current smokers represented across all terminal nodes should = 100% of smokers in the U.S adult population save possible rounding error.