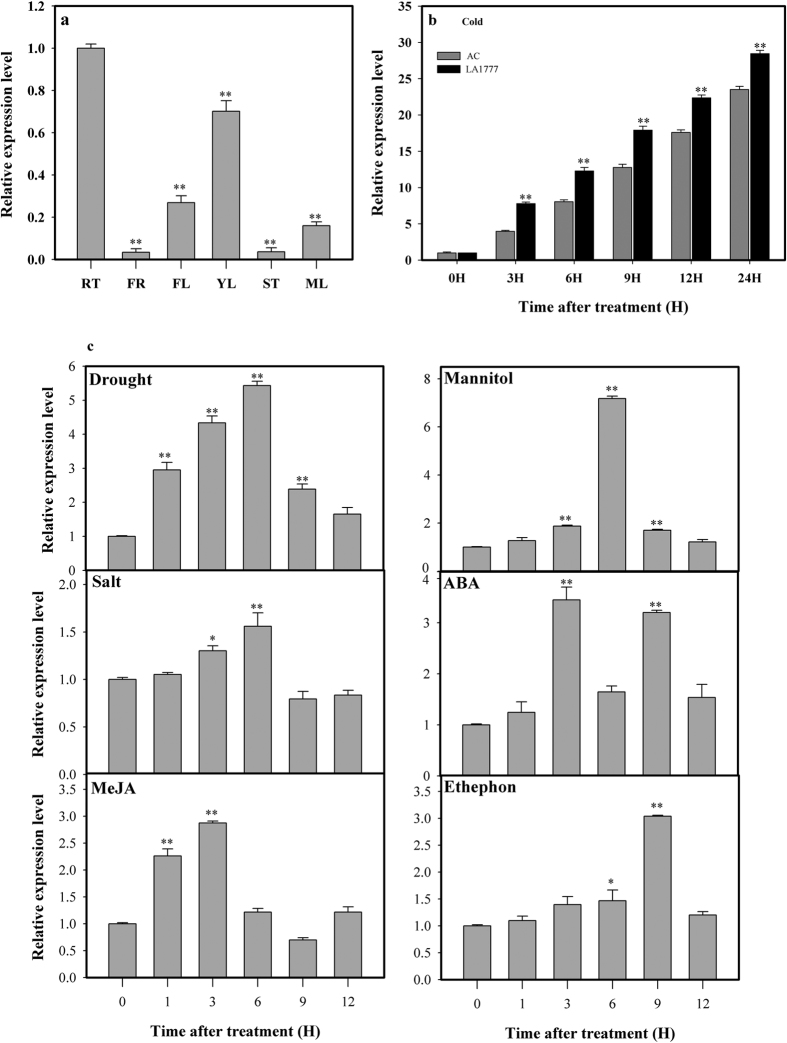
Figure 2. Expression patterns of CML44 under different treatments or various tissues.
(a) Expression pattern of ShCML44 gene in various organs (RT, root; FR, fruit, FL, flower, YL, young leaf; ST, stem; ML, mature leaf) of S. habrochaites LA1777 plants. Tissues were collected from six plants to perform qRT-PCR analysis. Asterisks indicate a significant difference (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test) compared with the root. (b) Comparative express level analysis of CML44 in S. habrochaites LA1777 and SlCML44 in S. lycopersicum AC under cold stress at 4 °C for 1, 3, 6, 9, 12, and 24 h. Zero (0) represents seedlings without any treatment. Asterisks indicate significant differences between LA1777 and AC at every time point. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, student’s t-test. ShCML44 expression pattern in LA1777 seedlings under treatments of drought (dehydration), salt (200 mM NaCl), and exogenous hormones (100 μM ABA, 100 μM MeJA, 100 μM Mannitol and 1% (v/v) ethephon) for 1, 3, 6, 9, and 12 h. Zero (0) represents seedlings without any treatment. Asterisks indicate a significant difference (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test) compared with the corresponding controls (0 h). For internal control, EF1α gene was used in qRT-PCR analysis. Values represent the means ± SE of three biological replicate samples. Each replicate sample was composite of leaves from three seedlings.