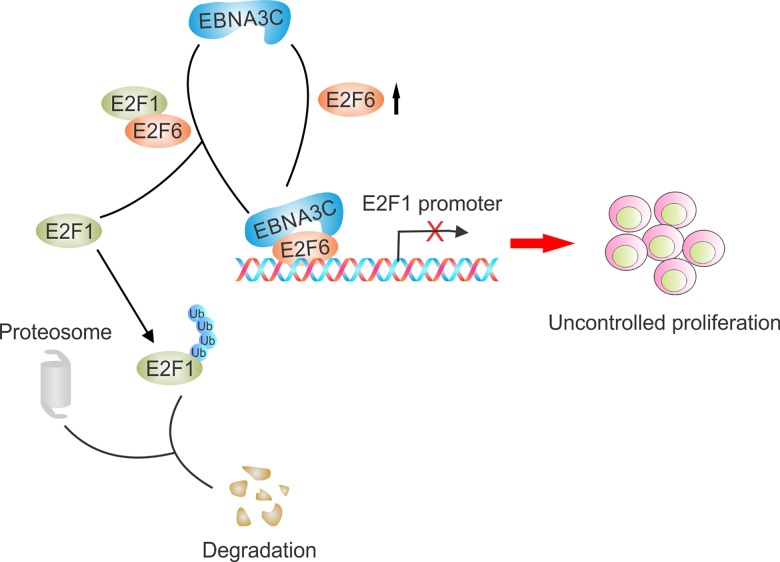
Fig 11. A schematic that illustrates the role of E2F6 in EBNA3C-mediated E2F1 regulation.
EBNA3C interacts with E2F6 specifically and enhances the stability of E2F6. EBNA3C can also compete with E2F1 for E2F6 binding. E2F6 recruited together with EBNA3C binds E2F1 promoter and inhibits its activity, which contributes to B-cell proliferation by reducing the expression of E2F1. This mechanism describes that the contribution of E2F6 in EBNA3C-related oncogenic activity important for EBV-transformed B-cell proliferation.