Figure 3.
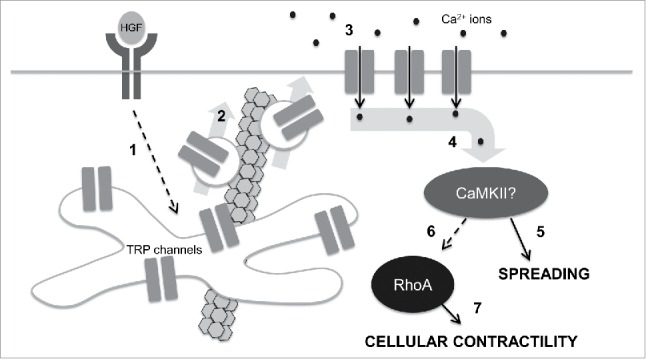
A speculative model for control of cell mechanics during epithelial scattering. In our model, 1.) HGF binding and activation of c-met receptor tyrosine kinases stimulates activates vesicle trafficking machinery in endosomal recycling compartments through an unidentified mechanism; 2.) Internal TRP channels are mobilized into vesicles that are destined for the plasma membrane in a microtubule-dependent vesicle trafficking step. 3.) TRP channels at the plasma membrane mediate a calcium influx that raises intracellular calcium concentrations. 4.) Intracellular calcium binds camodulin and in turn activates CaMKII. 5.) Early in epithelial scattering, CaMKII drives spreading, a result of reduced actin bundling at cell-cell junctions and myosin-based contractility. 6.) Late in epithelial scattering and through an as yet unidentified mechanism, CaMKII can stimulate an increase in RhoA activation. Seven. RhoA, through ROCK, increases myosin light chain phosphorylation, driving global cellular contractility and cell-cell detachment.
