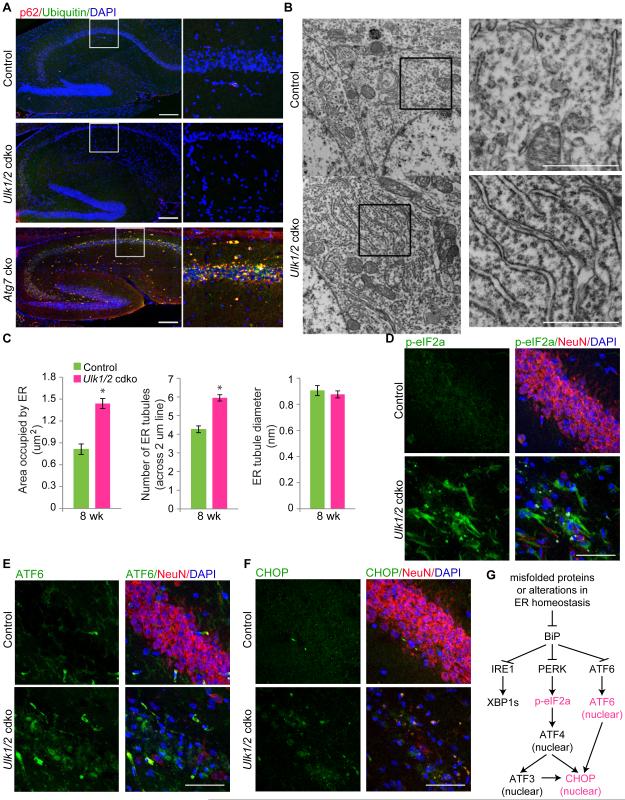
Figure 2. Ulk1/2 deficiency in hippocampal neurons is associated with activation of the UPR pathway.
(A) Representative images of brain sections from 4-wk-old Atg7-cko, 8-wk-old Ulk1/2-cdko and 8-wk-old control mice stained with antibodies against ubiquitin and P62, and counterstained with DAPI. Scale bars: 200 μm. (B) Representative electron micrographs of neurons in CA1 region from 8-wk-old mice. Scale bars: 1 μm. (C) Morphometric analyses of electron micrographs of hippocampal CA1 neurons from 8-wk-old control (n=2) and Ulk1/2-cdko (n=2) mice. *P <0.001 (Student's t-test). (D-F) Representative images of brain sections from the hippocampal region of16-wk-old mice stained with antibodies against p-eIF2α, ATF6 or CHOP, and counterstained with anti-NeuN. Sections were counterstained with anti-NeuN and DAPI. Scale bars: 50 μm. (G) Diagram of the UPR pathway, highlighting the activation of the PERK and ATF6 arms in the Ulk1/2-cdko mice. See also Figure S2.