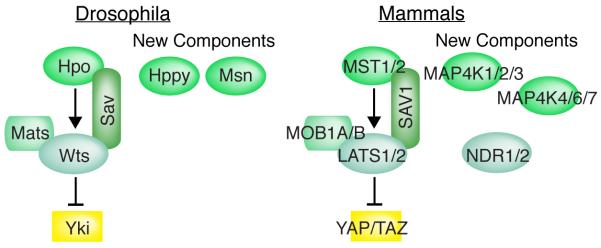
Figure 1. Core proteins of the Hippo network.
In Drosophila (left), the kinase Hpo phosphorylates and activates the kinase Wts; the kinase Wts phosphorylates and inhibits the transcriptional co-activator Yki. This requires the Wts co-factor Mats, and is facilitated by the scaffolding protein Sav. The Hppy and Msn kinases can also phosphorylate and activate Wts. In mammals (right), the kinases MST1 or MST2 phosphorylate and activate the kinases LATS1 and LATS2; the kinase LATS1 and LATS2 phosphorylate and inhibit the transcriptional co-activators YAP and TAZ. This requires the LATS co-factors MOB1A or MOB1B, and is facilitated by the scaffolding protein SAV1. MAP4K kinases can also phosphorylate and activate LATS kinases, and NDR kinases can also phosphorylate and inhibit YAP.