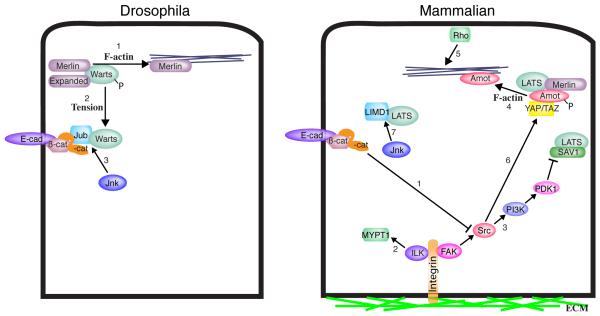
Figure 4. Regulation of Hippo signaling by F-actin and cytoskeletal tension.
Hippo signaling is regulated by levels of F-actin, tension within the actin cytoskeleton, and cell attachments. Several processes that could contribute to these effects have been identified, some of which are illustrated here. In Drosophila, these include 1) inhibition of Merlin-Wts interactions by F-actin, 2) cytoskeletal tension dependent recruitment of Wts into a complex with Jub at adherens junctions, and 3) promotion of Jub-Wts binding by Jnk phosphorylation. In mammals, these include 1) α-catenin-mediated inhibition of Src activation by integrins, 2) activation of MYPT1 by ILK, 3) inhibition of Sav-Lats association through a FAK-Src-PI3K-PDK1 pathway, 4) association of Amot with F-actin, which prevents Amot from associating with YAP/TAZ, 5) increases in F-actin promoted by Rho, 6) activation of YAP through phosphorylation of YAP by Src, and 7) promotion of LATS-LIMD1 binding by Jnk phosphorylation. In most cases potential conservation of these processes between Drosophila and mammals has not yet been investigated.