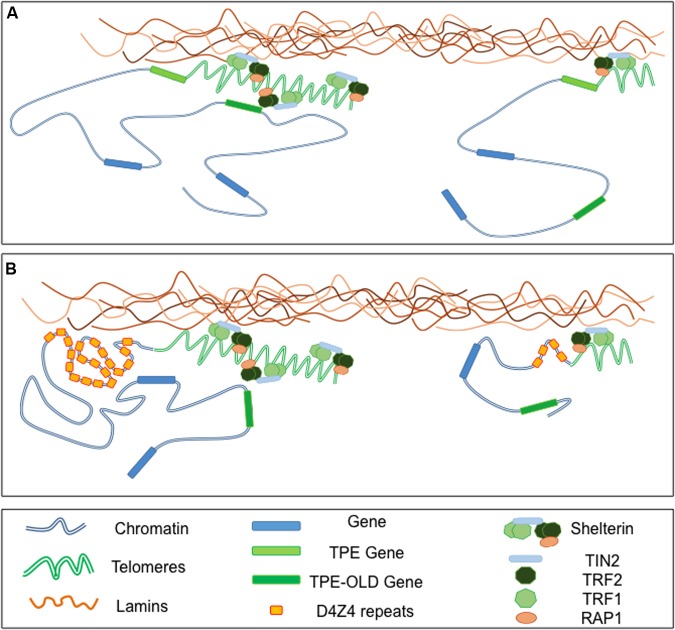
FIGURE 3.
Telomeres-Lamins interaction at the NP. (A) In cells with long telomeres, Lamins A/C interact with TRF2, thus tethering some telomeres in a peripheral localization. Telomeres might also interact with soluble Lamins in the nucleoplasm. The silencing signature of telomeres can spread in cis (TPE-sensitive genes) but also in trans (TPE-OLD-sensitive genes) due to a mechanism yet to explore. With telomeres shortening, the diminution of repressive mark (TPE) or a local change in the chromatin conformation (TPE-OLD), modulate expression of TPE and TPE-OLD genes. (B) Both TPE and TPE-OLD have been described in FSHD, a muscular dystrophy genetically linked to the subtelomeric 4q35 locus. This subtelomeric locus and its abutting telomere are located at the NP and regulated by A-type Lamins. Moreover, the number of D4Z4 repeats influences the localization of the telomeres within the nuclei. In cells with few D4Z4 repeats the transcription of DUX4, a gene encoded by D4Z4 repeats, is increased upon telomere shortening through direct TPE while expression of SORBS2, located 5 Mb upstream is up-regulated through a TPE-OLD phenomenon.