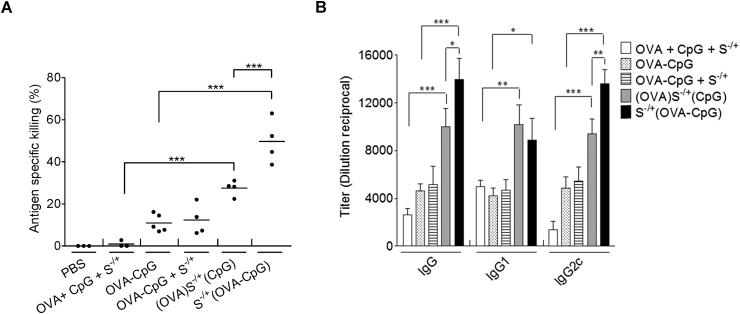
Fig. 3.
Assessment of immune response induced by (OVA)S−/+(CpG) or S−/+(OVA−CpG) in vivo. (A) Determination of the antigen−specific killing using in vivo CTL assay. C57BL/6 mice (n = 3–5) were immunized with the indicated treatments via footpad injection. Each treatment contained 6 μg of OVA. On day 7 following immunization, a 1:1 splenocytes mixture consisting of target cells pulsed with 200 nM SIINFEKL and labelled with 0.5 μM CFSE and unpulsed control cell labelled with 5 μM CFSE was intravenously administered to the control or immunized mice. Splenocytes were harvested, 18 h later, from the control or immunized mice and analyzed using flow cytometry analysis. Antigen−specific killing induced by each treatment was determined. Each dot represents killing of target cells by each mouse, the mean value for each treatment is shown as a horizontal bar. (B) Quantification of OVA−specific IgG. C57BL/6 mice (n = 3) were immunized with the indicated treatments, via footpad injection, each treatment contained 6 μg of OVA and CpG. On day 21 following injection, control or immunized mice sera were collected. The OVA−specific IgG, IgG1 or IgG2c were determined using ELISA. Data represent the mean value ± S.D. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.