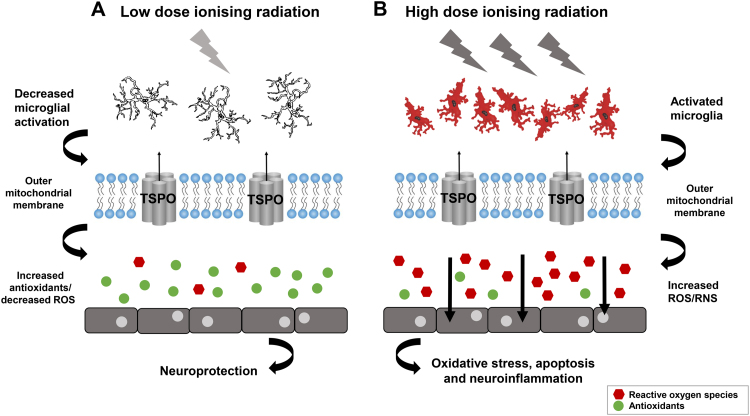
Fig. 3.
Ionising radiation and the cellular and molecular mediators of responses in the CNS. (A) Low dose ionising radiation may confer neuroprotection by decreasing neuroinflammation, increasing antioxidant levels and neutralising oxidative stress. (B) High dose ionising radiation provokes a neuroinflammatory response via activated microglia (cells in red), pro-inflammatory cytokines and reactive oxygen species (ROS) which can have deleterious effects on cell functioning and survival. The role of TSPO in modulating ROS may also implicate this protein in redox balance after ionising radiation at different doses. Adapted from [146], [147].