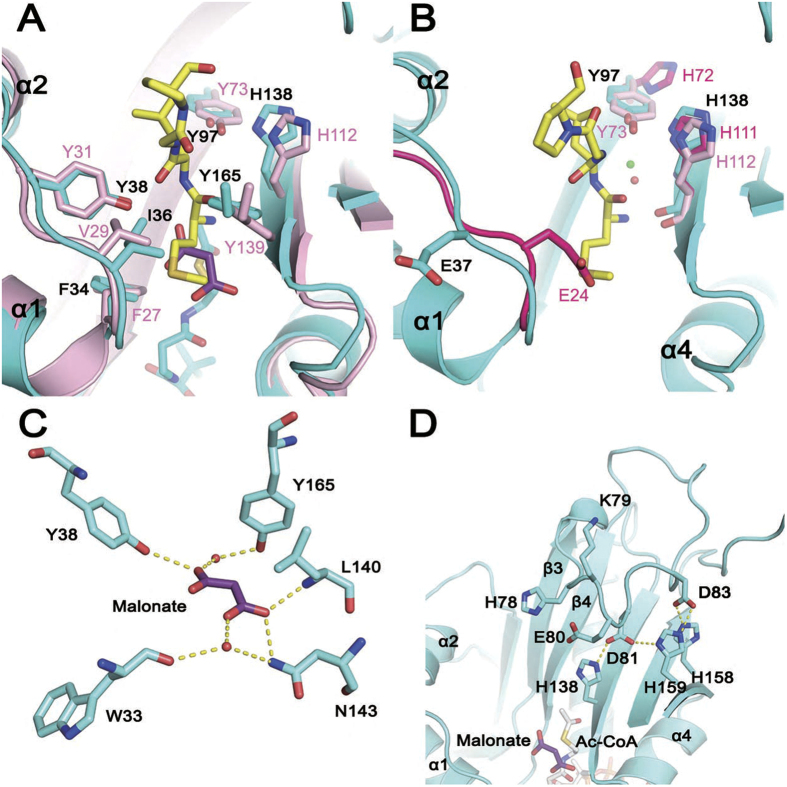
Figure 4. Structural basis for hNaa60 catalytic activity.
(A) Superposition of hNaa60 active site (cyan) on that of hNaa50 (pink, PDB 3TFY). Side-chains of key catalytic and substrate-binding residues are highlighted as sticks. The malonate molecule in the hNaa60(1-242)/Ac-CoA structure and the peptide in the hNaa50/CoA/peptide structure are shown as purple and yellow sticks respectively. (B) A close view of the active site of hNaa60. Residues Glu 37, Tyr 97 and His 138 in hNaa60 (cyan) and corresponding residues (Tyr 73 and His 112) in hNaa50 (pink) as well as the side-chain of corresponding residues (Glu 24, His 72 and His 111) in complexed formed hNaa10p (warmpink) are highlighted as sticks. The water molecules participating in catalysis in the hNaa60 and hNaa50 structures are showed as green and red spheres, separately. (C) The interaction between the malonate molecule and surrounding residues observed in the hNaa60(1-242)/Ac-CoA structure. The yellow dotted lines indicate the hydrogen bonds. (D) A zoomed view of β3-β4 loop of hNaa60. Key residues discussed in the text (cyan), the malonate (purple) and Ac-CoA (gray) are shown as sticks. The yellow dotted lines indicate the salt bridges.