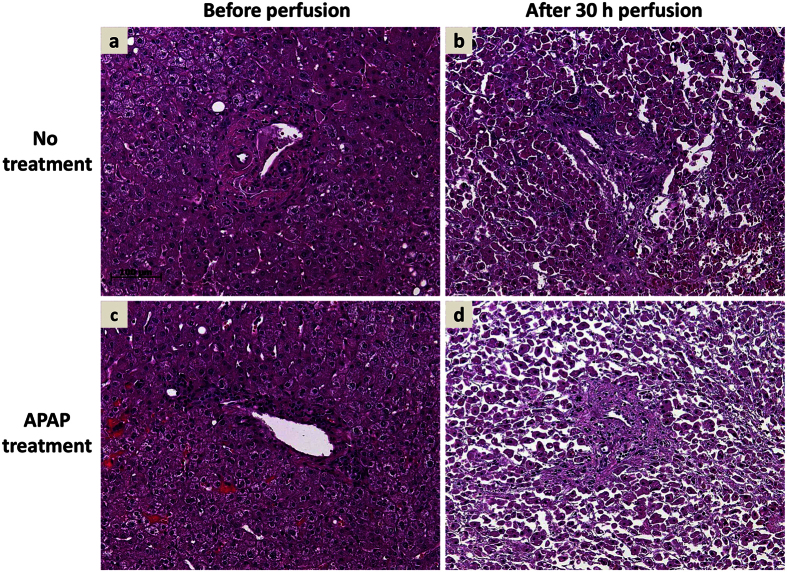
Figure 6. Liver perfusion causes tissue deterioration, which was aggravated by APAP poisoning.
Depicted are representative hematoxylin & eosin staining of matched liver tissue prior perfusion (a,c) and after 30 h of perfusion without treatment (b) or APAP treatment (d). While perfusion leads per se to deterioration of tissue integrity and cellular damage, large areas of confluent hepatocytes seem morphologically intact (b). Perfusion with APAP results in widespread tissue disruption, necrosis, and singularized cells without hepatocellular morphology. Sections a/b and c/d derive from the same liver specimen.