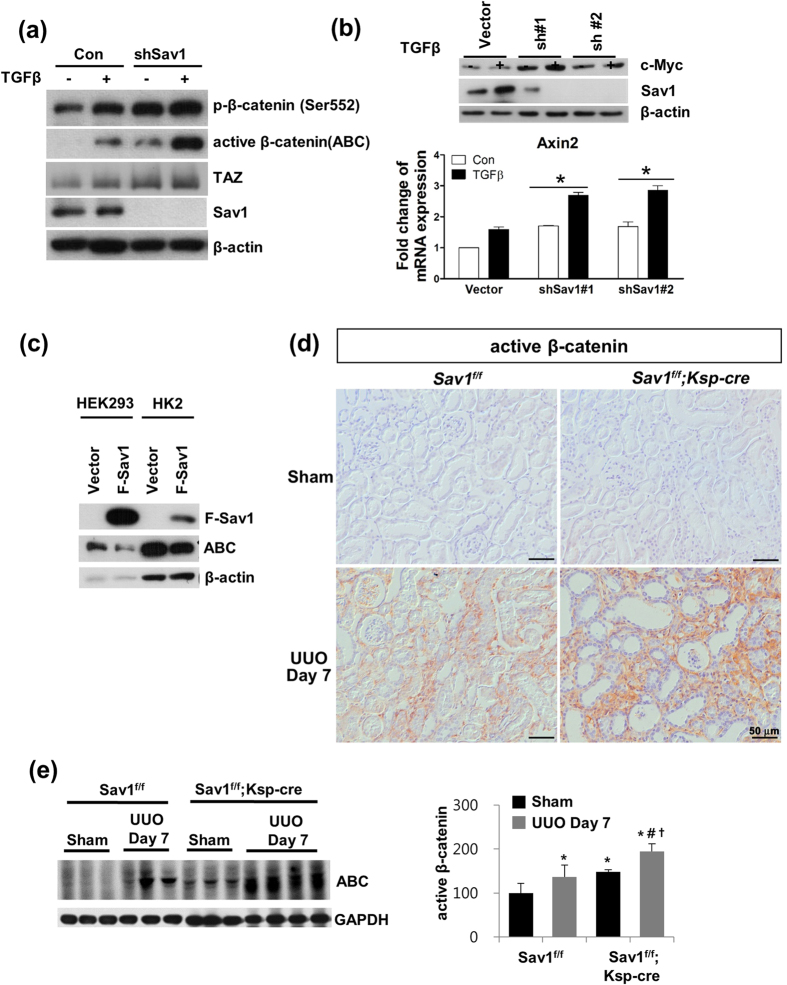
Figure 6. A Sav1 deficiency activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
(a) Western blot analysis of Ser552-phosphorylated β-catenin, unphosphorylated (active) β-catenin (ABC), TAZ, and Sav1 in control and Sav1-depleted HK2 cells with or without TGF-β1 treatment. Active β-catenin expression was enhanced by Sav1 deficiency and was increased by TGF-β1 treatment. (b) Expression of Wnt target genes c-MYC and AXIN2 in Sav1-deficient (shRNA #1 and #2) HK2 cells. Top: Western blot analysis of c-MYC expression. Bottom: qRT-PCR analysis of AXIN2 expression. c-MYC and AXIN2 expression was increased in TGF-β1-treated, Sav1-deficient HK2 cells. Error bars represent SEMs. *P < 0.05 by paired t-test (one-tailed). (c) Western blot analysis of active β-catenin expression in Sav1-overexpressing cells. HEK293 and HK2 cells were transfected with a Flag-Sav1 expression construct or vector control, and active β-catenin expression was detected. Sav1 overexpression reduced the level of active β-catenin expression. (d) Immunohistochemical staining for active β-catenin in the kidneys of WT and Sav1-null mice after UUO. Sav1-null mice kidneys stained strongly for active β-catenin after UUO. (e) Western blot analysis of active β-catenin expression in vivo. Active β-catenin expression was highly increased in the kidney tissues of TEC-specific, Sav1-null mice after UUO. Scale bar in d = 50 μm.