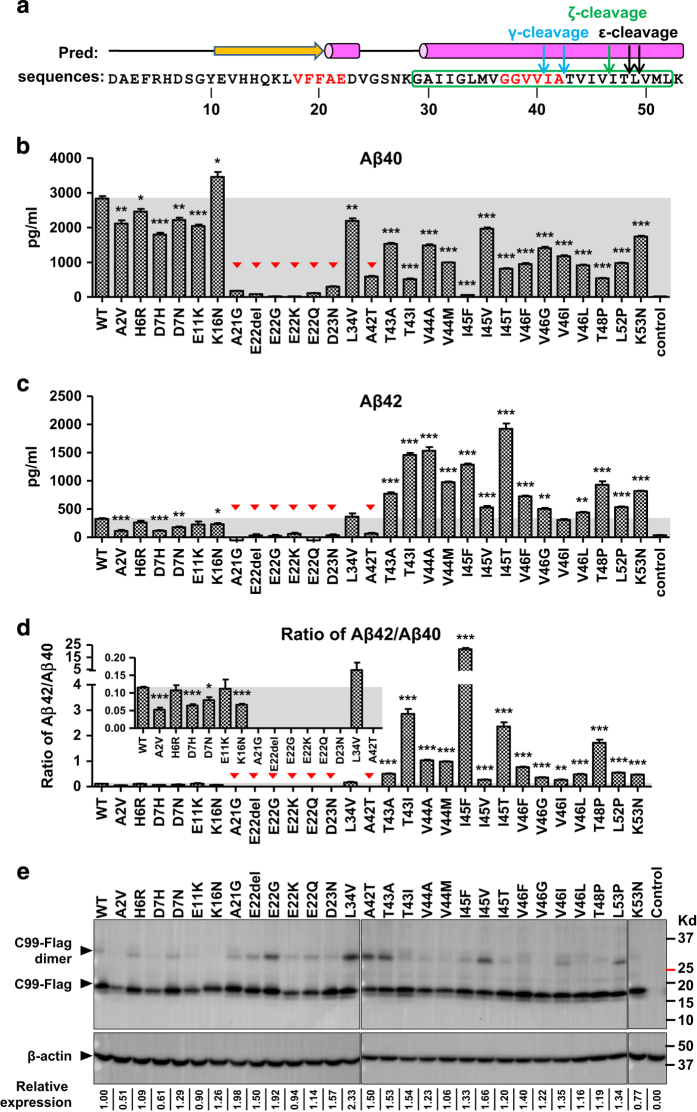
Figure 3.
FAD-linked C99 mutations that change amino acids C-terminal to the major γ-secretase cleavage site increase the Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio. (a) The sequence of the first 53 residues of C99 with predicted secondary structure elements, γ-secretase cleavage sites and the epitopes (red residues) recognized by AlphaLISA antibodies. (b) Concentration of the Aβ40 cleavage product as determined by AlphaLISA. See Supplementary Figure S6 for calibration graph. Mutations (residues A21 to D23 and A42) that affect amino acids within the epitopes recognized by the AlphaLISA detection antibodies are indicated by red triangles. (c) Concentration of the Aβ42 cleavage products as determined by AlphaLISA. See Supplementary Figure S6 for calibration graph. (d) The ratio of Aβ42 to Aβ40. The inlet shows the ratio at a different scale. The ratios are not presented for mutant proteins in which the mutation site is part of the epitopes. (e) Expression levels of C99 mutant proteins determined by anti-FLAG immunoblotting. Numbers below the immunoblot provide β-actin normalized signal relative to WT. Note that because of the sensitivity limitation of the assay (Aβ40: 88 pg ml−1; Aβ42: 300 pg ml−1), some of the Aβ42 signals were too close to background signal for reliable quantitation. See Supplementary Figure S9b and c for normalized amounts of Aβ40 and Aβ42 (error bars=s.e.m., n=3, *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001 (versus WT)).