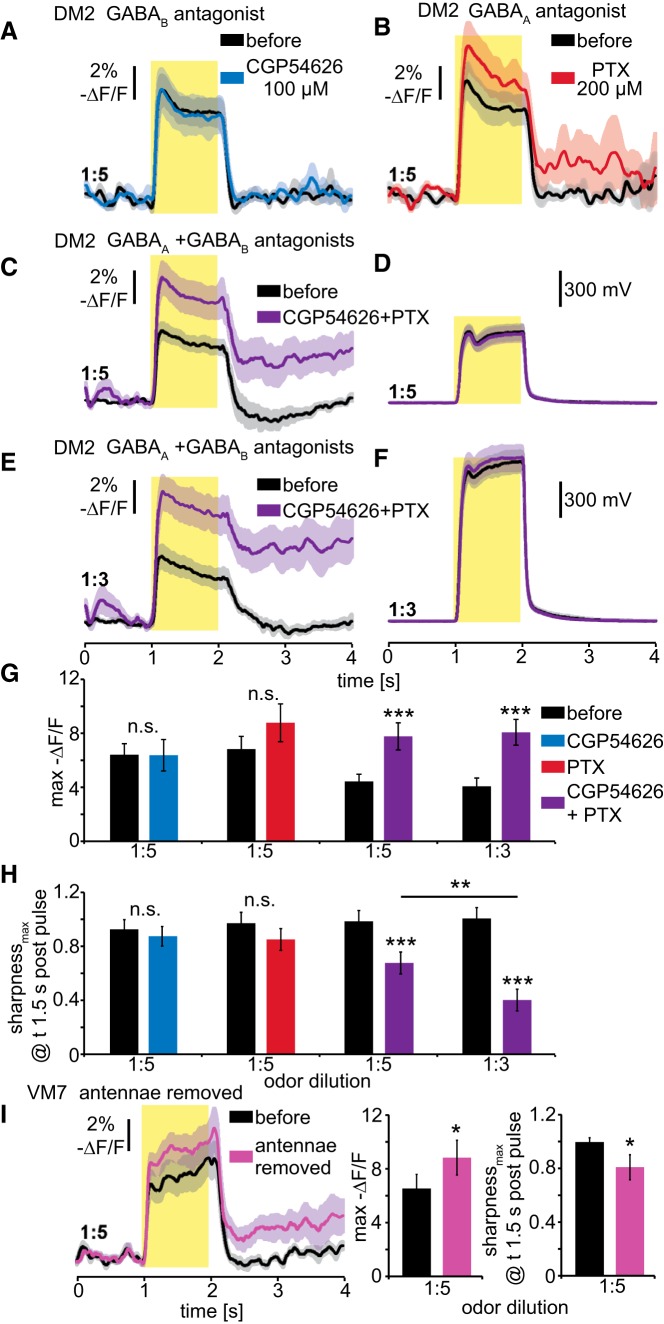
Figure 4.
Temporal contrast enhancement in OSN presynaptic terminals is mediated by GABAA and GABAB receptors. A, Pharmacological inhibition of GABAB receptors with CGP54626 has no effect on presynaptic electrical responses of OR22a-expressing OSNs in DM2 to a 1 s pulse of 1:5 Eb. Mean ± SEM; n = 5. B, Pharmacological inhibition of GABAA receptors with PTX appears to slightly increase magnitude and prolong presynaptic electrical responses in DM2 to 1 s pulses of 1:5 Eb. Mean ± SEM; n = 5. C–F, Simultaneous pharmacological inhibition of GABAA and GABAB receptors increases magnitude and prolongs presynaptic electrical responses in DM2 to 1 s pulses of 1:5 (C) and 1:3 (E) Eb. Simultaneously recorded PID signals are identical before and after drug application (D, F). Mean ± SEM; n = 9. G, Maximum presynaptic voltage responses indicate that only simultaneous pharmacological inhibition of GABAA and GABAB receptors significantly increases the magnitude of voltage responses. Mean ± SEM; n = 5 for CGP54626, n = 5 for PTX, and n = 9 for CGP54626+PTX. Statistical analysis: two-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test, ***p < 0.001. H, Sharpness coefficient indicates that only simultaneous inhibition of GABAA and GABAB receptors significantly reduces the temporal contrast enhancement of presynaptic voltage responses. The sharpness of responses to 1:3 Eb is reduced significantly more than that to 1:5 Eb, which is consistent with the larger sustained peripheral response to 1:3 Eb (Fig. 2F). Mean ± SEM; n = 5 for CGP54626, n = 5 for PTX and n = 9 for CGP54626+PTX. Statistical analysis: two-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test, **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. I, Removal of the antennae reduces lateral inhibition of the maxillary palp glomerulus VM7 (Olsen and Wilson, 2008). In response to 1:5 Eb, removal of the antennae increases presynaptic voltage responses and reduces sharpness. Mean ± SEM; n = 7. Statistical analysis: paired t test, *p < 0.05.