Figure 7.
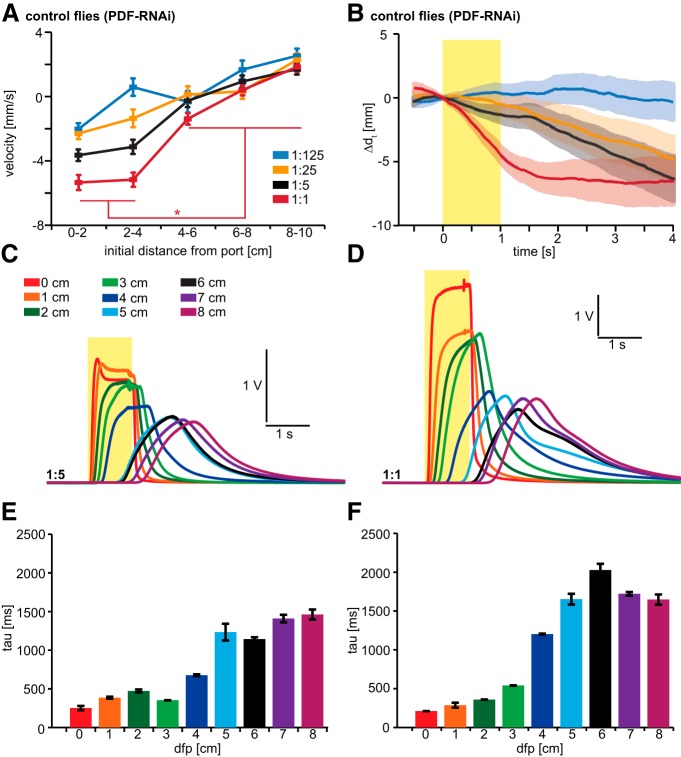
Behavioral responses to quick 1 s Eb pulses are dependent on temporal odor dynamics in the behavioral chamber. A, Velocity of flies during and after 1 s Eb pulses is dependent on initial position within the olfactory arena at initiation of the odor pulse. Control flies expressing PDF-RNAi in OR22a-expressing neurons exhibit strong avoidance only to 1:1 Eb and only when initial position in the arena is ≤4 cm from the odor port. Mean ± SEM; n = 116–172 total flies per genotype and concentration assayed in at least 10 independent experiments. Statistical analysis: two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test, *p < 0.05. B, Behavioral responses of control flies (initial position to port <5 cm) to 1 s Eb pulses of gas-phase dilutions, as indicated in A. Mean ± SEM. C, D, Mean PID recordings (n = 5) in the behavioral chamber showing odor dynamics of 1 s odor pulses of 1:5 (C) and 1:1 (D) that vary dependent on the distance to the odor port. E, F, Tau represents the time that the odor stimulus takes to reach 36.8% of its peak value. For 1:5 (E) and 1:1 (F), tau drastically increases after a distance of 3–4 cm from the odor port, indicating that flies within 3 cm from the odor port experience a fast increase and decrease in odor intensity, while flies that are >3 cm away from the odor port experience more gradual changes in odor intensity. Mean ± SEM. n = 5.