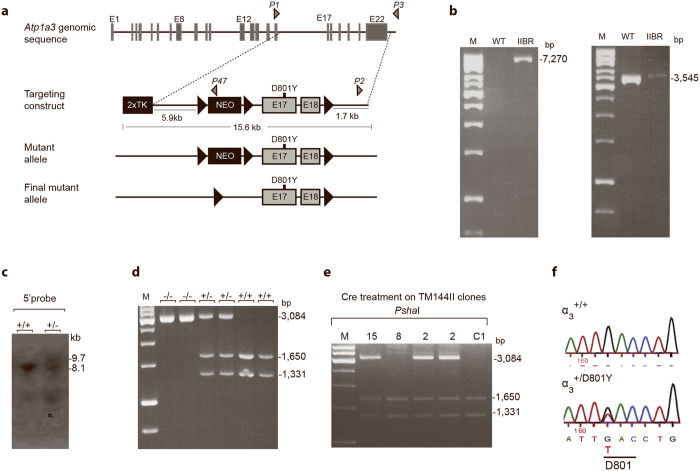
Figure 1. Generation and Targeting Strategy Screenings of the α3+/D801Y knock-in mice.
Diagram of the targeting strategy showing the oligonucleotide primers (grey triangles: P1, P2 and P3, P47, and P2) (a). PCR screenings verified homologous recombination in the IIBR clone, which was not observed for WT controls (b). Southern blotting analysis verified heterozygous homologous recombination in clone IIBR not observed for control (ES cells) (c). Partial Cre-excision of LoxP-NEO-LoxP cassette in the IIBR clone was verified by PCR and not observed for two controls (C1) (d) Confirmation of the third LoxP site was performed by a PshaI digest (a restriction site introduced with LoxP insertion) of a PCR product (using primers 5′-gtagccctgggattaaaggt and 5′gaagagaaggaggaatgaggg on genomic DNA). Treatment with the PhsaI enzyme gave in WT a non-digestable band of 2981 bp, and (+/−) gave 3084 bp, and 1650 bp and 1331 bp bands, whereas (−/−) gave 1650 and 1331 bp bands (e). Sequencing confirmed a heterozygous G → T base exchange in position 80 in the genomic DNA of a α3+/D801Y mouse that was not present in WT (f). M; molecular DNA marker, bp; base pair, H2O; No template control where DNA was substituted with water.