Fig. 2.
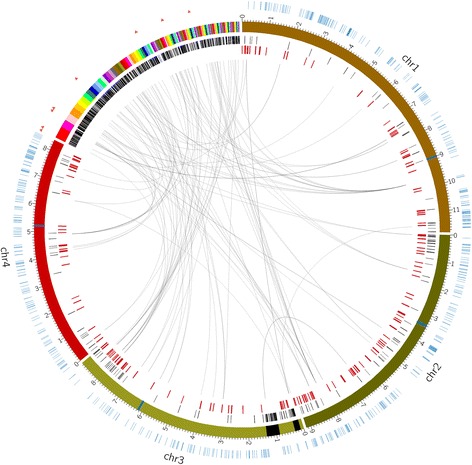
Circos plot showing differences between the core and supernumerary parts of the genome. Outer circle: blue lines denote the distribution of a MITE, red triangles denote ZIT1 copies. Second circle: core chromosomes and supernumerary contigs are colored, blue blocks on the chromosomes indicate the centromeres, black blocks show the two insertions of supernumerary sequence into the core chromosomes. Third circle: black lines represent intact (not RIPped) copies of TEs. Fourth circle: red lines represent RIPped copies of TEs. At the center of the plot, black lines connect gene duplications between the core genome and the supernumerary genome. Only protein hits larger than 266 amino acids are shown as their corresponding genes are supposed to be above the length threshold for RIP. Duplications within the supernumerary genome are not mapped
