Fig. 3.
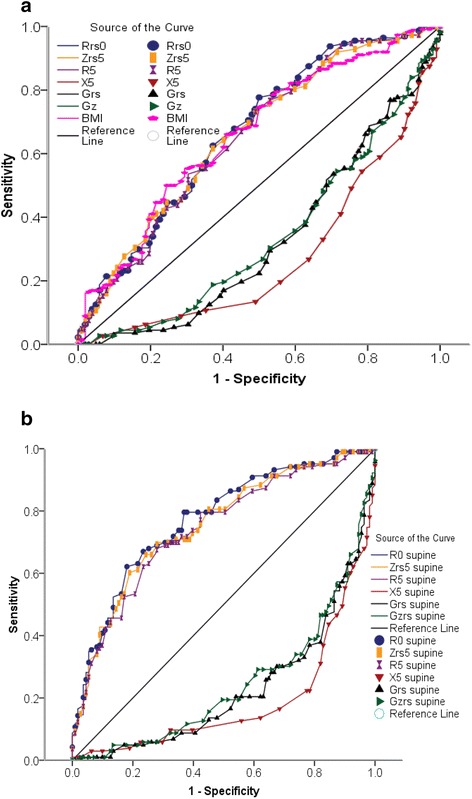
(a) ROC curves of the IOS parameters obtained in 93 patients suffering from OSAS and 121 non-OSAS patients in seated positions. The area under the ROC curve is a measure of the global ability of IOS parameter to correctly classify patients without and with OSAS (RDI < 15 or ⩾15/h). The value of the area under the ROC curve, respectively, for Rrs0 was 0.668 (95 % CI 0.596 to 0.740), for Zrs5 was 0.660 (95 % CI 0.587 to 0.732), R5 was 0.653 (95 % CI 0.580 to 0.727), BMI was 0.660 (95 % CI 0.588 to 0.733), Grs0 was 0.669 (95 % CI 0.596 to 0.741), Gz was 0.659 (95 % CI 0.587 to 0.732) and for X5 was 0.723 (95 % CI 0.655 to 0.792). (b) ROC curves of the IOS parameters obtained from all patients with and without OSAS in the supine position. The area under the ROC curve is a measure of the ability of IOS parameters to correctly classify patients of (RDI < 15 or ⩾15/h). The value of the area under the ROC curve for IOS parameters in the supine position, respectively, for Rrs0 was 0.772 (95 % CI 0.709 to 0.834), for Zrs was 0.754 (95 % CI 0.689 to 0.819), R5 was 0.743 (95 % CI 0.677 to 0.809), Grs was 0.772 (95 % CI 0.709 to 0.834), Gz was 0.754 (95 % CI 0.689 to 0.834) and for X5 was 0.811 (95 % CI 0.752 to 0.870)
