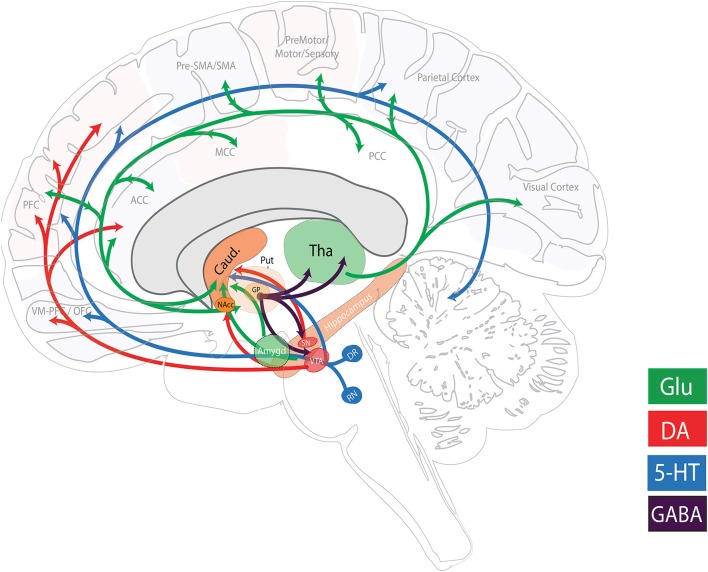
Figure 2.
Major neurotransmitter pathways related to GTS pathophysiology. Simplified schematic illustration of the major neurotransmitter systems reported and hypothesized to be involved in GTS pathophysiology. Other neuromodulatory systems that have been implicated include the cholinergic, histaminergic, and endocannabinoid systems. The figure was adapted based on information from Singer (2013) and Schumann et al. (2010). (5-HT, serotonergic; ACC, anterior cingulate cortex; Amygd, amygdala; Caud, Caudate nucleus; DA, dopaminergic; DR, dorsal raphe nucleus; GABA, gamma-aminobutyric acid; Glu, glutamatergic; GP, globus pallidus; MCC, mid cingulate cortex; NAcc, nucleus accumbens; OFC, orbitofrontal cortex; PCC, posterior cingulate cortex; PFC, prefrontal cortex; Put, putamen; RN, raphe nucleus; SMA, supplementary motor area; SN, substantia nigra; Tha, thalamus; VM-PFC, ventromedial prefrontal cortex; VTA: ventral tegmental area).