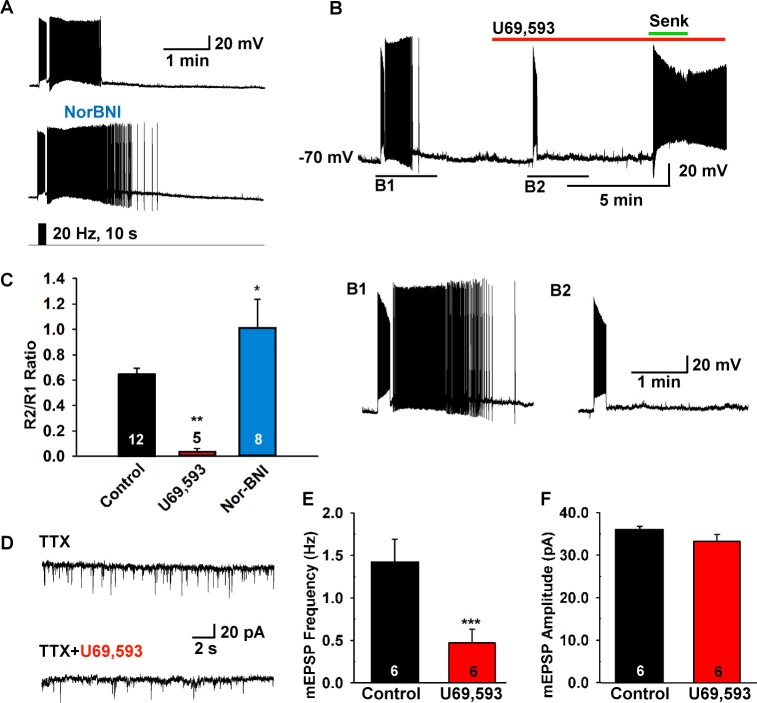
Figure 6. The κ-opioid receptor agonist blocks the slow EPSP.
(A–B) The κ-opioid receptor antagonist nor-BNI (1 μM) potentiated the slow EPSP (A) and the agonist U69,593 (1 µM) attenuated the slow EPSP (B2 versus B1). However, the Tacr3 agonist senktide is able to excite Kiss1ARH neurons in the presence of U69,593, indicative that the kappa-opioid effects are pre-synaptic to inhibit NKB release (B). (C) Bar graphs summarizing the effects of κ-opioid receptor agonist and antagonist on the slow EPSP. Comparisons between different treatments were performed using a one-way ANOVA analysis (F (2, 22) = 9.784, p = 0.0009) with the Newman-Keuls’s post hoc test. ** and * indicates p<0.01 and p<0.05 vs. control, respectively. (D–F) Effects of U69,593 on mEPSCs in Kiss1ARH neurons. Representative traces showing mEPSCs recorded at a holding potential of −60 mV under control conditions (TTX), and after TTX plus 1 µM U69,593. Summary data showing the effects of U69,593 on the frequency (E) and the amplitude (F) of mEPSCs in Kiss1ARH neurons (n = 6). Paired t-test, t(5) = 8.104, ***p<0.001 (E) and Paired t-test, t(5)=1.580, p = 0.1750 (F) compared to the control.