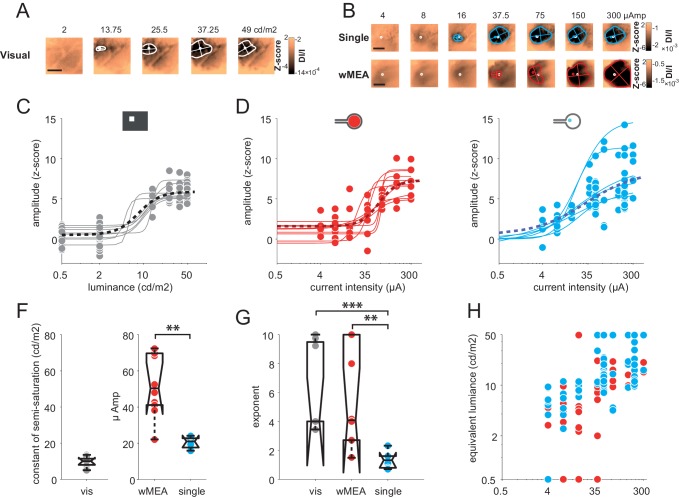
Figure 5. Intensity.
(A) V1 activation generated by visual stimuli of increasing luminance (value indicated above maps). Center-of-mass: white circle; extent: white contour; equivalent ellipse orientation and size of activation contour: white cross; scale bar: 2 mm. (B) V1 activation generated by SE (top) and wMEA (bottom) in 2 different animals at high current intensity. Center-of-mass of visual and electrical activations are indicated with white and colored circles respectively and extent of electrical activation in colored contours; scale bar: 2 mm. (C) Amplitude of cortical activation as a function of visual stimulus luminance computed over 8 rats (population fit: dashed black line; individual fits: gray thin lines). (D) Amplitude of cortical activations generated by wMEA stimulation at high current intensity. Population fit: dark red dashed line; individual fits: orange thin lines (N = 10). (E) Amplitude of cortical activations generated by SE stimulation at high current intensity. Population fit: dark blue dashed line (N = 25). Note that individual fits (cyan thin lines) were only performed on N=6 animals (tested with 7 different levels of intensity) and not on the others (N=19, tested with only 2 different levels: 50 and 200 µA). (F) Constant of semi-saturation (c50) for visual (gray in cd/m2) and electrical activations (wMEA: red and SE: blue, in µA). Two-sample Wilcoxon rank sum test: **p=0.0017, nSE = NSE = 6, nwMEA = NwMEA = 10. (G) Exponent of the naka-rushton fits for visual (gray) and electrical activations (wMEA: red and SE: blue). Two-sample Wilcoxon rank sum test: ***pSE vs. visual=6.66 10–4 (nSE = NSE = 6, nvisual = Nvisual = 8); **pwMEA vs. SE=0.0075 (nSE = NSE = 6, nwMEA = NwMEA = 10); pwMEA vs. visual=0.896 (nwMEA = NwMEA = 10, nvisual = Nvisual = 8). (H) Amplitude-based correspondence for all electrical activations to their visual counterpart (wMEA: red and SE: blue) as a function of current intensity level (in equivalent cd/m2).