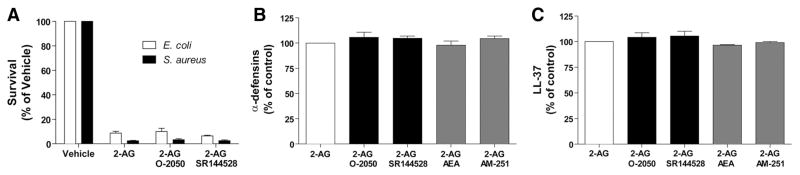
Figure 5. The 2-AG-mediated bacterial killing and antimicrobial peptide release are independent of CB activation.
(A) Neutrophil suspensions (2×107 cells/ml) in HBSS containing 1.6 mM CaCl2 were incubated with 1 μM cytochalasin B for 15 min and then stimulated with 1 μM 2-AG for 5 min. Incubations were stopped by adding 1 vol ice-cold buffer, immediately placing the samples in an ice-water bath for 5 min, and then centrifuged. Cell-free supernatants then were incubated with exponentially growing E. coli or S. aureus for 4 h and then plated on LB agar plates overnight to allow CFU quantification, as described in Materials and Methods. (B and C) Neutrophil suspensions (2×107 cells/ml) in HBSS containing 1.6 mM CaCl2 were incubated with 1 μM cytochalasin B for 15 min and then stimulated with 1 μM 2-AG for 5 min. Incubations were stopped by adding 1 vol cold incubation buffer and then rapidly centrifuged. Supernatants then were assessed for their content in (B) α-defensins 1–3 and (C) LL-37 by ELISA, according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Addition of 1 μM AEA, the GPR55 agonist (and CB1 antagonist) AM-251, the CB1 antagonist O-2050, or the CB2 antagonist SR144528 was done 5 min before stimulating neutrophils with 2-AG in all experimental settings. The data represent the mean (±SEM) of three independent experiments performed in duplicate.