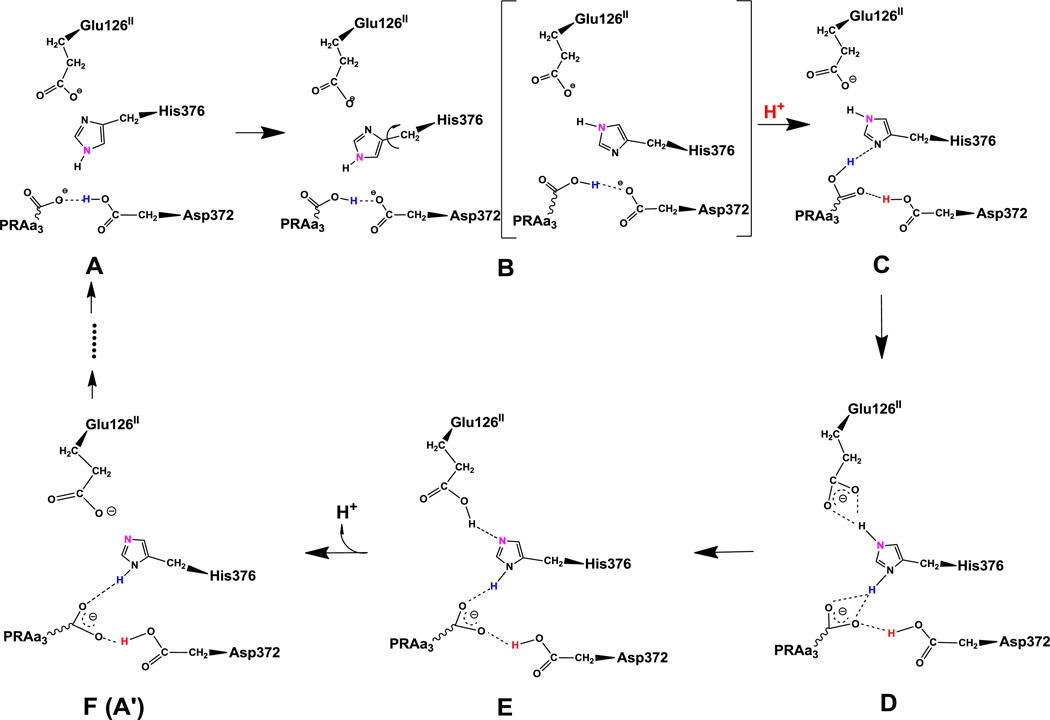
Figure 1.
Proposed proton transfer pathway. Protonation state D is the lowest energy protonation state for the investigated pre-pump state. Transferred protons and the ε-nitrogen on the imidazole ring of His376 are colored to guide the eye. (A) A strong hydrogen bond exists between protonated Asp372 and PRAa3, facilitating proton transfer. (B) Rotation of His376. (C) Proton uptake by Asp372 results in formation of a strong hydrogen bond between protonated PRAa3 and His376. (D) Proton transfer from PRAa3 to His376 results in a strong hydrogen bond between His376 and Glu126II. (E) Proton transfer from doubly protonated His376 to Glu126II and subsequent release into the water pool. (F) Structure and protonation state equivalent to (A) with exception of the orientation of His376 and protonation site δ-nitrogen.