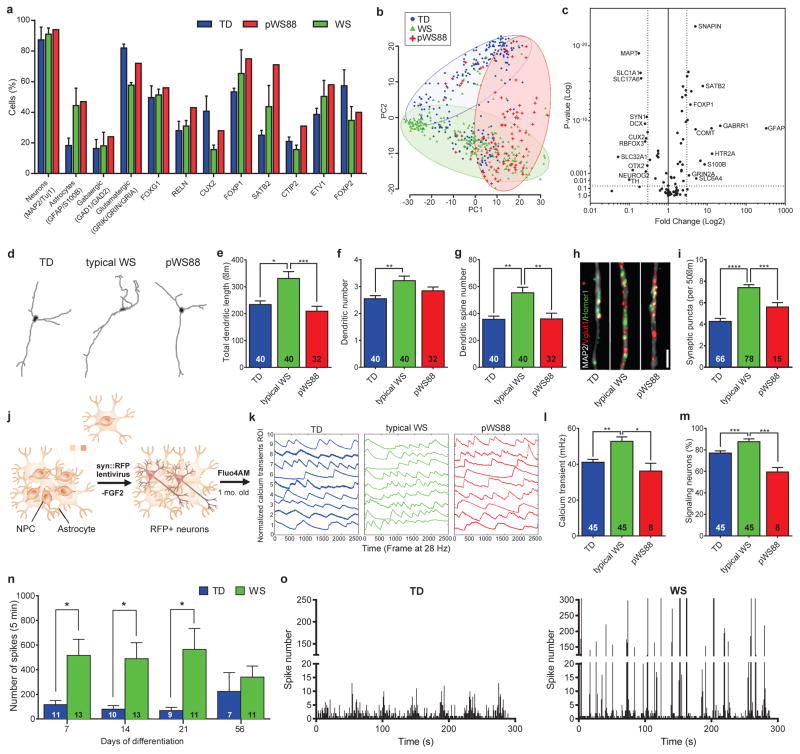
Figure 3. Altered morphology of WS-derived cortical neurons and network activity.
a, Percentage of cells expressing neural markers, neurotransmitter and cortical layer-related genes. WS, pWS88 and TD iPSC-derived neurons show non-significant percentage of cells expressing target genes over defined control Ct value. b, PCA of 672 cells projected onto the first two components. Overlaid populations of TD, pWS88 and WS neurons are shown. c, Volcano plot illustrates differences in expression patterns of target genes of iPSC-derived neurons from the single cell analyses. The dotted lines represent more than or equal to 3.0-fold differentially expressed genes between the groups at P<0.05 (unpaired Student’s t test). d, Representative images of tracings from TD, typical WS and atypical pWS88 iPSC-derived neurons (Syn::eGFP- and CTIP2-positive neurons). e–g, Morphometric analyses showing significant differences between TD, typical WS and pWS88 in total dendritic length (e), between TD and typical WS in dendrite number (f) and between TD, typical WS and pWS88 in dendritic spine number (g). h and i, Puncta quantification of post- and pre-synaptic markers. Scale bar, 2 μm. For e–g and i, data are shown as mean ± s.e.m. n = number of traced neurons. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001, Kruskal-Wallis test and Dunn’s multiple comparison test (e–g), one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post hoc test (i). j, Schematic diagram summarizing preparation of neurons for calcium transient analysis. k, Representative images of the calcium tracing from iPSC-derived neurons. Fluorescence intensity changes reflecting intracellular calcium fluctuations in neurons in different Regions of Interest (ROI). l and m, Typical WS-derived neurons exhibited significant increase in calcium transient frequency (l) and percentage of signaling neuron in the culture (m) when compared to TD or pWS88 neurons. Data are shown as mean ± s.e.m. n = number of fields analyzed; 3198 neurons for TD, 4446 neurons for WS and 48 neurons for pWS88. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, Kruskal-Wallis test and Dunn’s multiple comparison test. n, MEA analyses revealed an increase in spontaneous neuronal spikes in WS during differentiation compared to TD. o, Although the number of total network bursts do not differ, WS shows a higher number of spikes in each burst compared to TD. Data are shown as mean ± s.e.m. n = number of MEA wells analyzed *P<0.05, **P<0.01, two-sided unpaired Student’s t test.