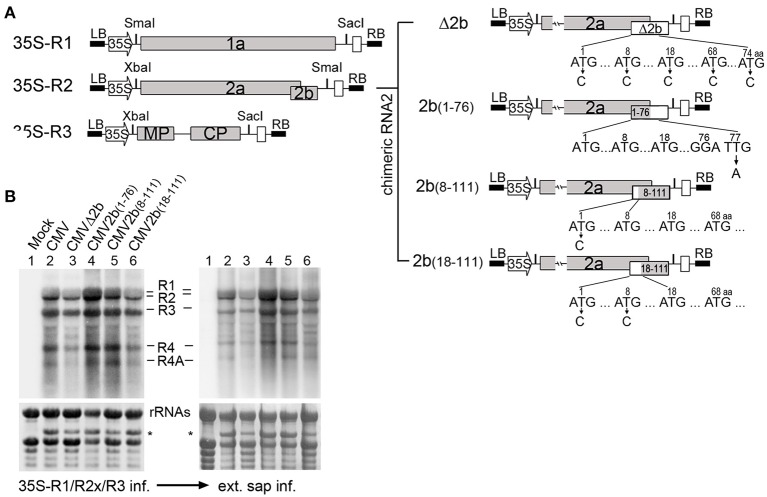
Figure 1.
Construction and biological activities of 2b mutants in the context of CMV infection. (A) Diagram of SD-CMV infectious clone construction. 35S-R1, 35S-R2, and 35S-R3 were the three full-length clones of SD-CMV genomic RNA1, RNA2, and RNA3 as well as four chimeric RNA2 mutants. R2aΔ2b, 2b protein expression was abolished; R2a2b(1–76), with deletion of the C-terminal 35 amino acids; R2a2b(8–111), with deletion of the N-terminal seven amino acids; and R2a2b(18–111), with deletion of the N-terminal 17 amino acids. Substituting “C” for each “T” in the start codon ATG, as well as other ATG codons, or “A” for “T” in creating stop codon present in the 2b coding sequence are indicated with the numbers of the amino acid positions. (B) RNA gel blot detection of CMV accumulation in Agrobacterium-inoculated leaves (left panel) and the plants inoculated with sap extracted from each CMV2b(x)-infected Nb leaf (right panel). SD-CMV genomic RNA 3′ UTR was used as a probe. Methylene blue-stained ribosomal rRNA was used as loading control. *A stained viral RNA used as an indicator of SD-CMV infection.