Figure 2.
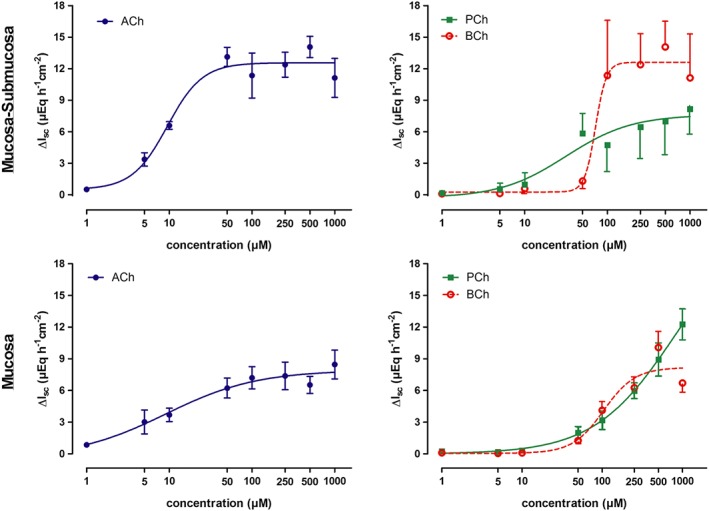
Concentration‐dependent increase in I sc across mucosal–submucosal preparations (1st row) and mucosal preparations (2nd row) from rat distal colon induced by serosal administration of acetylcholine, propionylcholine or butyrylcholine. Because of the desensitization of the I sc response at higher concentrations, all three choline esters were only administered once to an individual tissue when used in concentrations ≥100 μM, whereas for lower concentrations, they could be administered repeatedly to the same tissue with a washing step between the individual administrations (Methods). The curves show fits to a Hill equation. Hill coefficients were in the range of 0.8–2.2 with the exception of the response to butyrylcholine in the mucosal–submucosal preparation, where the Hill coefficient was 6.6 (for EC50 values, see text). Values are given as increase in I sc (ΔI sc) above baseline just prior administration of the respective agonist concentration and are means (symbols) ± SEM (vertical lines). n = 5–8. ACh, acetylcholine; BCh, butyrylcholine; PCh, propionylcholine.
