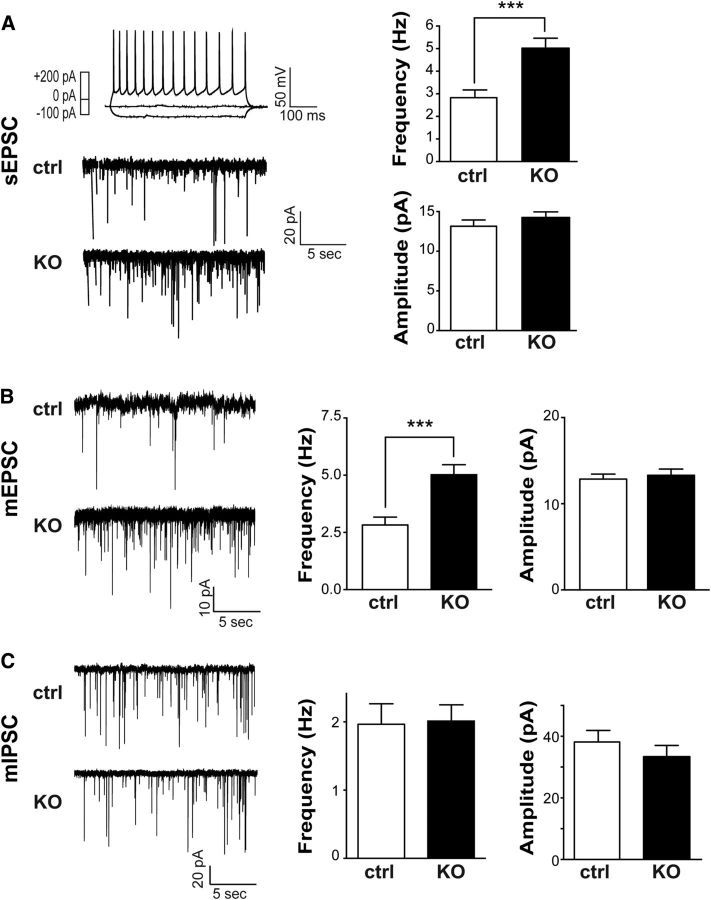
Figure 7.
mGluR5 in glutamatergic neurons modulates the amount of excitatory inputs they receive. A, Example recordings of sEPSCs in cortical layer IV neurons of mosaic animals. Top, Right, AP pattern evoked by various current injections reveals a characteristic response of a spiny stellate excitatory neuron. Bottom, Left, Example traces of sEPSCs recorded from nonfluorescent control neurons or tdTomato-labeled KO neurons. Right, Summaries of the frequency and amplitude of sEPSCs. B, Left, Representative traces of mEPSCs from control and mGluR5 KO neurons. Right, Summaries for the frequency and amplitudes of mEPSCs. C, Left, Representative traces of mIPSCs from control and mGluR5 KO neurons. Right, Summaries for the frequency and amplitudes of mEPSCs. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (***p < 0.001, compared with mGluR5f/f, Student's t test). ctrl, control; pA, picoamps; mV, millivolt; ms, millisecond; sec, seconds; Hz, hertz.