Figure 2.
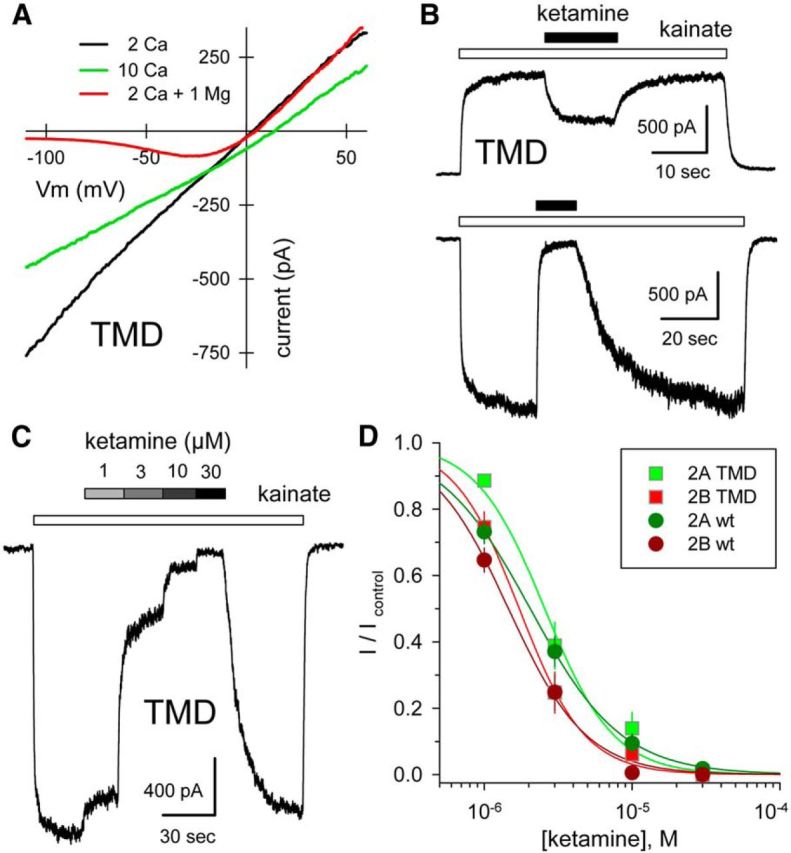
Calcium permeability and ketamine block of chimeric channels. A, Whole-cell current evoked by 10 μm NMDA plus 10 μm glycine as a function of voltage as membrane potential was ramped from −110 to +60 mV at 0.75 mV ms −1 in 160 mm NaCl, 10 mm HEPES with 2 mm CaCl2 (black), or with 10 mm CaCl2 (green), or with 2 mm CaCl2 and 1 mm MgCl2 (red). Note the rightward shift in reversal potential in elevated calcium. GluN1/2A TMD. B, Exposure to 30 μm ketamine (black bars) blocks current evoked by 10 μm kainate (open bars) at −80 mV, and to a lesser extent at +40 mV. GluN1/2A TMD. C, Whole-cell current evoked by 10 μm kainate is blocked progressively by 1, 3, 10, and 30 μm katamine. GluN1/2A TMD. D, Current in the presence of ketamine as a fraction of control (mean ± SEM) is plotted as a function of ketamine concentration. Smooth curves are best fits of 1/(1 + [(ketamine)/IC50]n) where IC50 is the concentration producing half-maximal inhibition and n is the slope factor. Values for chimeric constructs (N1/2A: IC50 = 2.6 ± 0.2, n = 1.9 ± 0.3, 7 cells; N1/2B: IC50 = 1.7 ± 0.1, n = 2.0 ± 0.3, 9 cells) were not significantly different from those of the respective wild-type subunits (N1/2A: IC50 = 2.0 ± 0.1 μm, n = 1.4 ± 0.2, 13 cells; N1/2B: IC50 = 1.6 ± 0.2, n = 1.7 ± 0.2, 10 cells) by t test.
