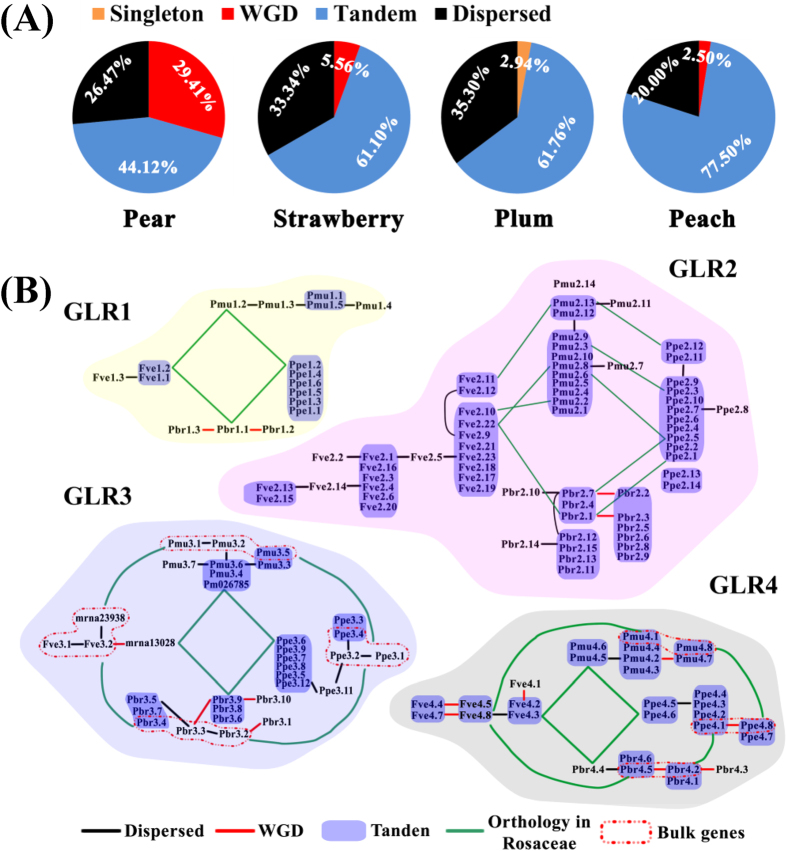
Figure 3. Expansion analysis of GLR gene family in Rosaceae genomes.
(A) The quantification statistics for different duplication events in Roseceae GLRs. Initially, the BLASTP algorithm was used to search for potential homologous GLR gene pairs (E < 1 e−5, top five matches) across entire genome. Secondly, these homologous pairs were used and inputted into MCScanX to identify syntenic chains. The GLRs locate in a syntenic block were defined as WGD/segments duplication; The GLRs neighbouring less than 10 genes were defined as tanden duplication; and the remainders of homologous GLRs were defined dispersed duplication. (B) Orthology and duplicate path analysis of GLR genes in four Roseceae species. We assembled the duplicated gene pairs to form a linear expansion in each Rosaceae species based on hypothesis tests on the nearest duplicated gene pair’s performance characteristics, which included the highest identity (Table S4), maximum number of flanking genes in segments and the lowest synonymous mutations (Table S5). Orthology GLRs were identified in MCScanX program.