Fig. 10.
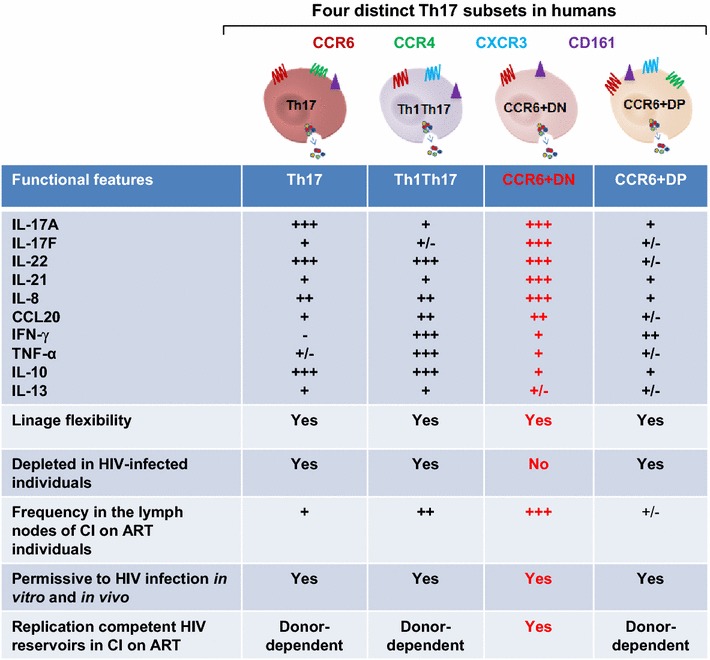
New insights into the heterogeneity of human Th17 cells at homeostasis and during ART-controlled HIV-1 infection. In this work we identified two new subsets of CCR6+ T-cells, CCR6+DN/CCR4−CXCR3− and CCR6+DP/CCR4+CXCR3+, that share Th17 features with the previously described Th17/CCR4+CXCR3− and Th1Th17/CCR4−CXCR3+ [5]. Despite these similarities, CCR6+DN distinguished from the other three subsets by superior their ability to produce Th17 effector cytokines (e.g., IL-17F, IL-8, and IL-21) and their predominant frequency/counts in the blood and lymph nodes HIV-infected individuals receiving ART. Finally, we demonstrate that CCR6+DN harbor replication-competent HIV-DNA. Thus, we reveal the existence in humans of four Th17-polarized CCR6+ subsets that represent distinct stages of Th17 differentiation, with CCR6+DN being the most predominant and contributing to HIV reservoir persistence under ART
